
Book a Consultation
Thank you!
Your form has been sent successfully.



May 10, 2023
Adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) is a rare form of cancer, typically arising in the salivary glands. But this form of cancer can also occur in other parts of the body such as the lungs, breast, and skin. It is slow-growing cancer with a tendency to invade nerves and blood vessels, and a high rate of recurrence even after treatment.
According to the American Cancer Society, this cancer accounts for less than 1% of all cancers. The incidence of ACC occurring in other parts of the body is much lower, with fewer than 500 cases diagnosed each year.
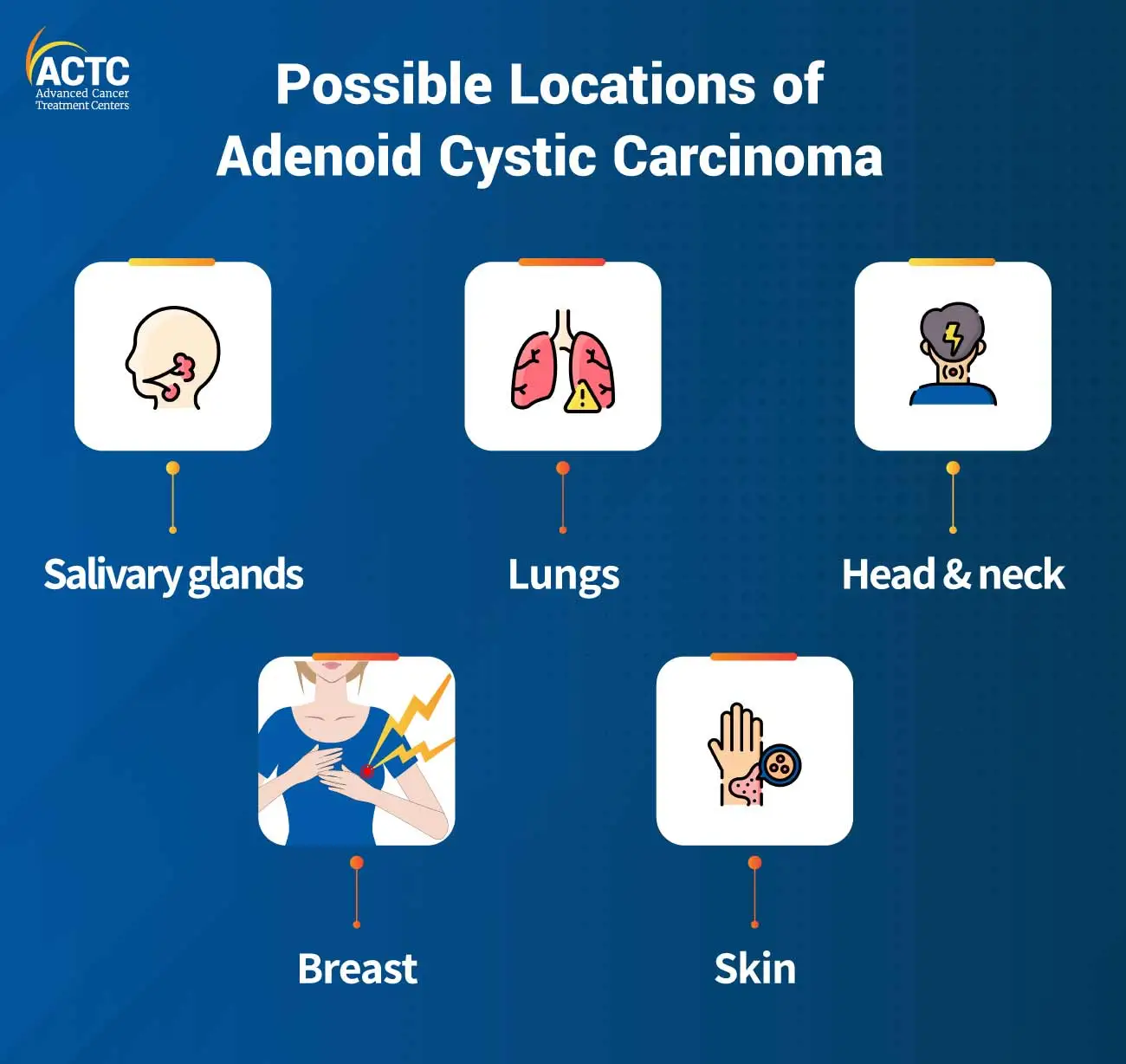
The signs and symptoms of Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma (ACC) vary depending on the location of the tumor.
ACC in the lungs may not cause symptoms at the early stage. As the tumor grows, symptoms may include coughing, chest pain, shortness of breath, and wheezing.
Those having ACC in breast may experience a painless lump, skin thickening or dimpling, nipple retraction or discharge, and changes in breast size or shape.
ACC in the head and neck region can cause symptoms such as a lump or swelling, difficulty swallowing, changes or hoarseness in voice, and pain or pressure in the ear.
ACC of the skin may appear as a nodule or sore that does not heal. People may also experience thick, scaly patches on skin that may bleed or crust over time.
According to the American Cancer Society, some people with ACC may not experience any symptoms at all until the cancer has advanced. In case of any symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
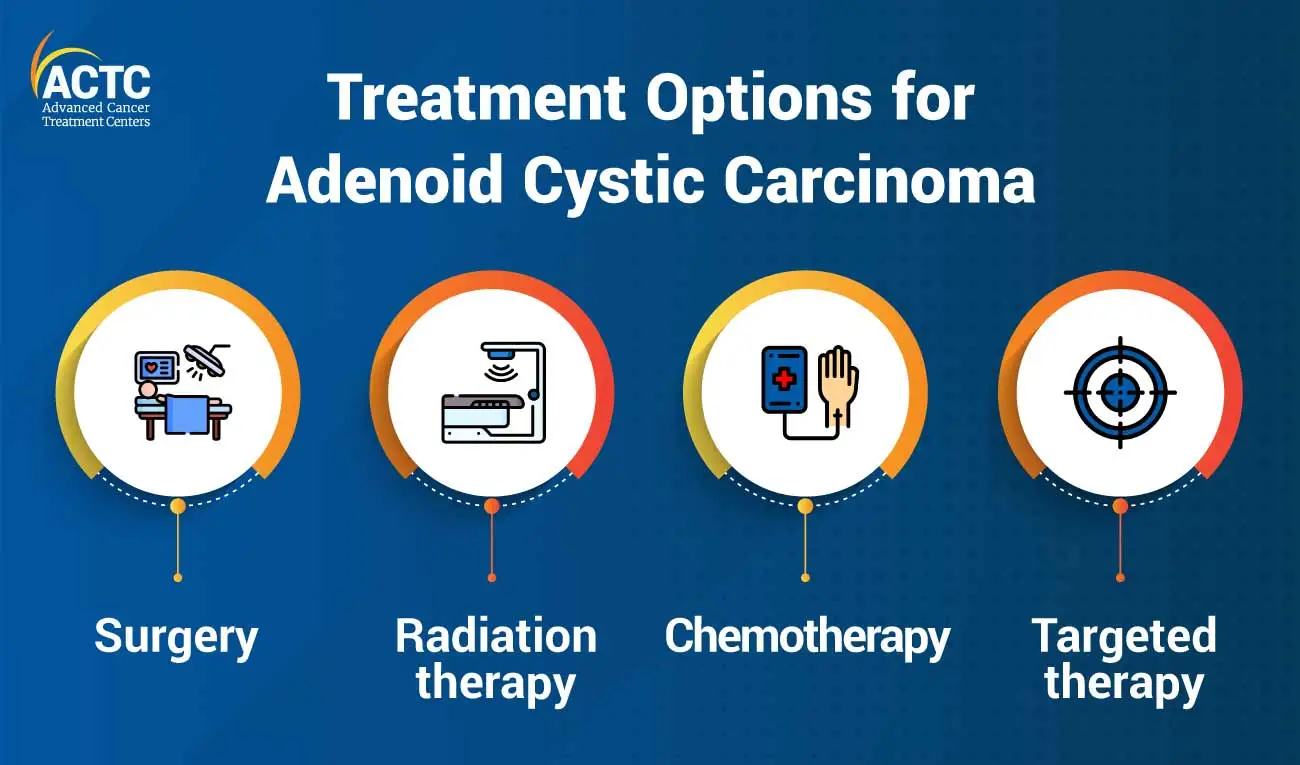
ACC is considered a challenging cancer to treat due to its complex biology and location-specific treatment considerations. Treatment options for ACC depend on several factors, such as the location of the tumor, its size, stage, and whether it has spread to other parts of the body. The following are some common treatment options for ACC:
It is the most common treatment option recommended by oncologists for ACC. The goal of surgery is to remove the tumor and surrounding tissue affected by cancer. In some cases, a surgeon may perform a minimally invasive procedure, such as endoscopic surgery to remove the tumor. In more advanced cases, complicated surgical procedures, such as a radical neck dissection or a mastectomy, may be required.
This treatment option uses high-energy x-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy may be used before surgery to shrink the tumor or post-surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells. In some rare cases, radiation therapy is used as the main treatment when surgery is not possible.
This is a common cancer treatment option that uses drugs to kill cancer cells. But chemotherapy is not often used to treat ACC because it is not as effective as surgery or radiotherapy. However, in some cases, chemotherapy may be used in combination with other treatments to effectively treat ACC.
It is a type of cancer treatment that targets specific molecules or proteins involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells. The type of targeted therapy recommended for ACC depends on the specific molecular and genetic characteristics of the tumor.
However, it is critical to note that the effectiveness of targeted therapies is still being studied. Therefore, the choice of targeted therapy and its effectiveness should be discussed with a healthcare provider in detail.
The choice of treatment depends on several factors, and a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including surgeons, medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, and other specialists, should be involved in the decision-making process to create the most effective treatment plan.
Although ACC is rare, it is a form of cancer that is difficult to treat. The 5-year survival rate for ACC is 80.4%, 10-year survival rate is 61.3% and 15-year survival rate is 29.4%.
Research has also revealed that individuals with a history of ACC are likely to be monitored for the rest of their lives even if their treatment is successful. The recurrence rate is extremely high and 75% of cancers come back within 10 years.
Unfortunately, there is no known way to prevent adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) at present. Although the exact cause of ACC is unknown, it is believed to be related to genetic mutations or changes in certain genes that regulate cell growth and division.
However, individuals can reduce their risk of developing any type of cancer in general by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding exposure to known carcinogens, and getting regular check-ups with their primary care physician to detect any potential issues early.
Since adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) is a rare form of cancer, routine screening is not currently recommended for the general population. However, individuals with a family history of ACC may benefit from close monitoring and regular check-ups with their healthcare provider to detect any potential issues early.
Early detection and diagnosis of ACC can help improve outcomes for individuals. Therefore, it is important for individuals to be aware of the symptoms of ACC and to seek medical attention immediately if they experience any concerning signs or symptoms. For any concern related to adenoid cystic carcinoma, contact ACTC, one of the best cancer treatment centers in Florida and consult our expert providers.


January 07, 2026
A chemo port is a small device placed under your skin that makes recei...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
It's natural to wonder if testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is sa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A rash that will not calm down is scary, especially when it changes or...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Florida’s lung cancer burden remains significant and affects many fa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A partial hysterectomy, also called a supracervical hysterectomy, is s...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Finding a rash on your breast can be unsettling, but remember, many ra...
KNOW MORE
