
Book a Consultation
Thank you!
Your form has been sent successfully.

Testicular cancer is a rare form of cancer diagnosed in men, accounting for only 1% of all cancer cases. It develops when abnormal cells in the testes begin to divide and grow in an uncontrolled manner. These malignant (cancerous) cells can develop in the tissues of one or both testicles, whereas in benign tumors, it grows in a single location and does not spread. Though it can impact males of any age, it is mostly found in men between the ages of 15 and 44. If detected early, it is mostly curable.
The most common type of testicular cancer occurs in the form of a germ cell tumor (GCT). There are two main types of GCT’s: seminoma and nonseminomatous germ cell tumors.
Seminomas are most commonly found in the testes. They can also be found in other parts of the body such as the brain, chest, or belly. Seminomas grow and spread in a slower fashion than nonseminomas cancers. Seminomas produce human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) which are tumor indicators that can induce illness signs and symptoms.
Nonseminomatous malignancy starts in the cells that make sperm or eggs. Germ cell cancers of this type are more common in men in their late teens and early thirties. Nonseminomatous tumors are most commonly found in the testicles or ovaries. They are also found in the brain, chest, or belly.
The initial indicators of testicular cancer are usually an enlarged testicle or a tiny lump or patch of hardness. Consult your doctor as soon as possible if you notice a lump, enlargement, hardness, discomfort, or tenderness in the groin area. Sometimes, symptoms may appear after the disease has spread to other areas of the body.
Testicular tumor symptoms include:
 Dull ache or severe pain in the testicles or scrotum
Dull ache or severe pain in the testicles or scrotum
 A non-painful lump or enlargement on one of the testicles
A non-painful lump or enlargement on one of the testicles
 Heaviness in the scrotum or a change in the way a testicle feels
Heaviness in the scrotum or a change in the way a testicle feels
 Increase or decrease in the size of the testicle
Increase or decrease in the size of the testicle
 Sudden fluid accumulation in the scrotum
Sudden fluid accumulation in the scrotum
 Back pain
Back pain
The treatment option is determined by considering several criteria, including the stage of the illness and your personal preferences.

Surgical removal of the affected testicle is the first line of treatment for all types of testicular cancer, regardless of stage. If it has not spread, this could be your only option. In the event that the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes, your doctor will likely remove them by surgery.
Seminoma cancers can be treated with radiation therapy. This treatment uses high-powered energy beams to destroy cancerous cells. Your fertility may be affected if you undergo radiation therapy.
Chemotherapy is another systemic mode of treatment. If the cancer has spread, chemotherapy is the only treatment before or after surgery. In this process, chemotherapy drugs are administered throughout the body to destroy cancer cells.

The first sign of testicular cancer is typically a bump in the testicle. Some men find the lump on their own, while others discover it during a physical examination at their doctor's office.

If you have a lump in your testicle, your doctor will perform tests to determine if it is cancerous.
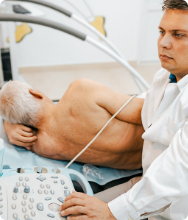
An ultrasound of your scrotum will be performed first. This may reveal whether the lump is solid or fluid-filled, as well as whether it is inside or outside the testicle.

Doctors might run a blood test to screen for tumor markers. These are chemicals in your blood that may become more prevalent if you have cancer.
The testicular cancer doctors at ACTC, are committed to providing exceptional patient care by prescribing effective, tailored, and evidence-based treatment strategies. Throughout the cancer journey, we attempt to provide a supportive environment for patients and their families, focusing on both physical and mental wellness.
The following are our providers who you can consult at ACTC:

MD, Hematology & Oncology

MD, Ph.D., Hematology/ Medical Oncology

MD, Radiation Oncologist

Cancer patients look for a sense of trust and care once diagnosed. At ACTC, we make it our priority to make them feel secure and optimistic about the journey ahead. Our state of the art mechanisms and dedicated team of specialists are there at all times for support. Right from staging to treatment to long term follow up, we ensure that no hurdle is faced by them at any point. We have a team of qualified and experienced cancer specialists along with clinical staff with over 2 decades of experience in personalized treatment and cancer care.
Schedule a consultation by calling
 352-345-4565
352-345-4565
Testicular cancer can be successfully treated. While a cancer diagnosis is always frightening, the good news is that testicular cancer is treated effectively in 95% of instances.
The three basic forms of treatment for testicular cancer are chemotherapy, radiation, and surgery. The treatment method depends on the type of testicular cancer that has been diagnosed : seminoma or non-seminoma.
Pain or discomfort in a testicle or the scrotum. Testicular cancer is typically not painful. However, for some men, pain in the testicle or scrotum may occur.
Schedule a consultation by calling
 352-345-4565
352-345-4565