
Book a Consultation
Thank you!
Your form has been sent successfully.

Skin cancer is the most frequently diagnosed form of cancer in the United States. It occurs when cells in the outer layer of your skin (epidermis) grow uncontrollably.
Normally, skin cells grow to replace older cells that die, but skin cancer starts when this balanced process fails.
Skin growths may be non-cancerous (benign), meaning they don't spread, or they can be cancerous (malignant), meaning they can grow deeper and spread if not detected and treated early. Early detection is key to effective treatment.
Skin cancer has three main types: squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, and melanoma.

Each type starts in different cells within the epidermis. Most skin cancers can be treated effectively when caught early.
Squamous cell carcinoma usually isn't life-threatening but can be aggressive. It starts in the flat cells near the skin’s surface, which are regularly shed as new cells form. It's categorized as a non-melanoma skin cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma begins in the deepest (basal) layer of the epidermis. Basal cells divide frequently to replace skin cells that wear away on the surface.
It typically develops on areas exposed to the sun, such as your face, and is also a non-melanoma skin cancer.
Melanoma is less common but can be more serious. It develops from melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin, which gives skin its color and protects deeper layers from sun damage.
Melanoma can spread to other parts of the body and can be life-threatening if not found early.
Skin cancer commonly appears on sun-exposed areas like the face, scalp, arms, hands, and legs, but it can also occur in areas rarely exposed to the sun, including your palms, under fingernails or toenails, and the genital area.
Watch for these common signs:
A shiny, red, pink, or clear bumpOther warning signs include:
A white or yellow waxy patch with unclear bordersIf you notice any of these, seek medical evaluation promptly.
Diagnosing skin cancer begins with your doctor carefully examining any suspicious spots, noting their size, shape, color, texture, and any bleeding or scaling. They may also check nearby lymph nodes for swelling and refer you to a dermatologist (skin specialist) for further testing.
A biopsy (tissue sample) is usually taken to confirm the diagnosis. Your doctor numbs the area first, and in some cases, removing the entire growth during the biopsy can be enough to treat the cancer.
If there’s concern that the cancer has spread, your doctor may recommend imaging tests
to check your internal organs and bones. Imaging procedures are painless, non-invasive
(no incision), and commonly include:
CT scan
X-ray
MRI
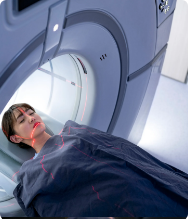
Abnormal imaging results may lead to a more targeted biopsy to confirm spread.

Doctors use several types of treatments to manage skin cancer. The specific treatment recommended depends on the cancer type, size, location, and whether it has spread. Your doctor will discuss the most suitable options with you.
Surgery is the most common way to remove skin cancers. Mohs surgery, or Mohs micrographic surgery, involves removing thin layers of tissue and checking each layer under a microscope.
The process continues until no cancer cells are seen at the margins, ensuring healthy tissue remains.
Radiation therapy targets skin cancer from outside your body using beams of radiation. Doctors typically use low-energy X-rays or electrons, which reach only shallowly beneath your skin, minimizing harm to surrounding tissues.
Chemotherapy involves medicines given either by vein or orally. These drugs travel throughout your bloodstream, attacking cancer cells that have spread beyond the skin.
Regular follow-ups with your medical oncologist after chemotherapy are important to track treatment progress.
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) uses special medicines activated by specific types of light to destroy cancer cells. It's also known as photoradiation therapy, phototherapy, or photochemotherapy.
Immunotherapy harnesses your body's immune system to fight cancer cells. It’s particularly useful for advanced skin cancers. There are many FDA-approved immunotherapy options available for skin cancer today, with new treatments emerging regularly
Targeted therapy uses medicines designed to interfere with specific genes or proteins that help cancer cells grow and survive.
Some targeted therapies can also change the environment around cancer cells, such as blocking the growth of blood vessels that tumors need to grow.
Chemical peels are used to treat actinic keratosis, a precancerous condition that can progress into squamous cell carcinoma. In some cases, chemical peels may help treat facial warts, especially when applied by a trained dermatologist.
Many additional drug therapies are available for skin cancer, and new treatments are actively being tested in clinical trials.
The expert team at ACTC in Florida delivers top-tier cancer care through individualized treatment plans grounded in the latest medical evidence.
Our goal is to support your entire well-being—physical and emotional—so you feel cared for at every step of your cancer journey.
Meet our trusted providers at ACTC, each ready to offer expert guidance and care:

Hematology/Oncology

Hematology/Oncology

Radiation Oncology
At ACTC in Florida, our expert cancer specialists work alongside a deeply experienced clinical team, many of whom bring over two decades of knowledge to your care.
We’re here to guide you every step of the way—diagnosis, treatment, and beyond—all in one convenient, comforting place.
Call 352-345-4565 or book an appointment.

As one of Florida's leading advanced skin cancer centers, we understand how a cancer diagnosis and treatment impact a person's physical and emotional well- being. Therefore, we work hard to make patients and their families feel secure. We provide comprehensive treatment for all forms of skin cancer at ACTC, including screening, diagnosis, staging, treatment, and long-term follow-up, all in one convenient location. Our physicians are backed up by qualified clinical staff with over two decades of experience and a reputation for providing individualized treatment.
Schedule a consultation by calling
 352-345-4565
352-345-4565
If a mole biopsy comes back positive for melanoma (skin cancer), your doctor will assess how deeply it has grown or whether it has spread. Next, they will create a personalized treatment plan based on your specific diagnosis and stage of the disease.
Symptoms that skin cancer has spread vary based on the type and location of the cancer. For melanoma, common signs of spreading may include:
Chronic coughing or trouble breathing if it spreads to your lungs
Headaches or seizures if it moves to your brain
Swollen lymph nodes or unusual lumps under your skin
Always tell your doctor immediately if you notice new or worsening symptoms.
Checking your scalp is very important because skin cancer there can easily go unnoticed. To examine your scalp properly:
Use a mirror or ask someone else to look closely at your scalp regularly.
Feel for unusual bumps, sores, or rough patches with your fingers.
Tell your doctor if you notice any new or changing spots or growths.
Regular scalp checks help catch skin cancer early when it’s easier to treat.
Schedule a consultation by calling
 352-345-4565
352-345-4565