
Book a Consultation
Thank you!
Your form has been sent successfully.

According to the American Cancer Society, gallbladder cancer is rare cancer that occurs when gallbladder cells multiply and grow abnormally. The gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ located under the liver. It stores and releases the bile enzyme that is produced by the liver. Bile contains bile salts, cholesterol, bile acids, and pigment bilirubin that help in the digestion of fats. Bile also helps in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, such as vitamins A, D, E, and K.
Based on the origin of the cancerous cells, gallbladder cancer types can be classified as:
Adenocarcinoma is the most common form of gallbladder carcinoma that develops in the gland-like cells of the gallbladder's lining. Different types of adenocarcinoma of the gallbladder are:
This form of cancer develops in the squamous cells located on the lining of the gallbladder.
It occurs in both the gland-like cells and flat squamous cells of the gallbladder's lining.
Sarcoma is an aggressive cancer that develops in the connective tissue of the gallbladder.
Common signs and symptoms of gallbladder cancer may include:
 Generalized yellowing of the skin (jaundice)
Generalized yellowing of the skin (jaundice)
 Stomach pain
Stomach pain
 Fever
Fever
 Nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting
 Abdominal lump
Abdominal lump
 Bloating
Bloating
Gallbladder cancer treatment options depend on the type and stage of the disease and the overall health of the patient.
According to the National Cancer Institute, surgery involves the complete removal of the gallbladder and some tissues around it. The procedure is called a cholecystectomy. Depending on the location and size of the tumor, gallbladder cancer doctors may perform a minimally invasive surgical technique called laparoscopic surgery.
This therapy uses high-energy radiation to kill cancerous cells to treat gallbladder carcinoma. Radiation can be delivered via an external machine outside of the body, called external beam radiotherapy.
Chemotherapy uses systemic anti-cancer drugs, which enter the bloodstream and reach and destroy rapidly growing abnormal cells.
Immunotherapy, also called biologic therapy, enhances the immune system's ability to target and destroy cancerous cells.
Targeted drug therapy explicitly targets specific cell proteins or genes that block the growth and spread of this disease. It causes fewer side effects and spares healthy cells because of its specific action.
Various methods are used for a definitive gallbladder cancer diagnosis after considering the patient's symptoms, age, and general health.
Blood samples are tested to check the liver function by measuring the levels of liver enzymes and tumor markers specific to gallbladder cancer.

Endoscopic ultrasound or endo-sonography uses a probe attached to a thin, flexible, lighted tube called an endoscope. It is inserted into the body through the mouth or rectum. The probe uses high-energy sound waves to create an image of the gallbladder and nearby organs.
It is an imaging technique to detect any blockage in the passage (bile ducts) through which liver enzymes pass from the liver/gallbladder to the intestines. Different types of cholangiography are:

A biopsy is a definitive cancer diagnosis that includes removing a tissue sample for microscopic examination. According to the American Cancer Society, a gallbladder biopsy is not always performed before surgery. The biopsy may be performed postoperatively after surgical removal of the tumor. If cancer can not be surgically removed, the biopsy may be done using a fine needle to remove tissue fluid or cells from the suspicious area (FNAC).
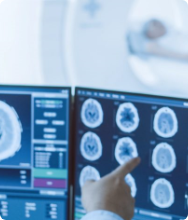
High-intensity radiation is used to produce detailed 3-dimensional computerized images. They are used to locate and measure the tumor's size. Various imaging tests used are:
The oncologists at ACTC in Florida are dedicated to providing exceptional patient care by prescribing effective personalized and evidence-based treatment plans for their patients. We strive to establish a positive environment for patients and their families throughout their cancer journey, simultaneously focusing on physical and mental health. We have some of the most accomplished cancer specialists working on our team.
The following are our providers who you can consult at ACTC:

MD, Hematology & Oncology

MD, Ph.D., Hematology/ Medical Oncology

MD, Radiation Oncologist

If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with gallbladder cancer, a detailed discussion with your primary physician will help you understand your condition better. Your primary care doctor can then refer you to an advanced specialty center such as ACTC in Florida.
As one of Florida's best cancer centers, we understand how a cancer diagnosis and therapy impact a person's physical and emotional well-being. Therefore, we work hard to make patients and their families feel secure. We understand how imperative it is for you and your loved one to make informed choices and play an active part in your medical care. We at ACTC strive to support you at every step of diagnosis, staging, treatment, and long-term follow-up in one convenient location. Our cancer specialists are supported by qualified clinical staff with over two decades of experience and a reputation for providing personalized gallbladder cancer treatment.
Schedule a consultation by calling
 352-345-4565
352-345-4565
There are several factors that determine the prognosis (chances of recovery) of gallbladder cancer. They include the patient's general health and age, location of the tumor, metastasis of the tumor, type of tumor, or if cancer has recurred.
According to the American Cancer Society, gallstones, calcium deposits on the gallbladder, obesity, older age, cysts in bile ducts, gallbladder polyps, and familial history of cancer are the risk factors for this cancer.
It is hard to detect gallbladder cancer in its initial stages as it does not show any early symptoms. The gallbladder is located below the liver, so it is difficult to observe during a routine physical examination.
Schedule a consultation by calling
 352-345-4565
352-345-4565