
Book a Consultation
Thank you!
Your form has been sent successfully.

Prostate cancer is common, especially as men get older, typically after age 50. The prostate gland is a small, walnut-sized organ just below the bladder that produces part of the fluid in semen.
As men age, the prostate usually grows larger, and sometimes cells in or around the gland start growing abnormally, which can lead to cancer.
Many prostate cancers grow slowly, meaning they might not cause symptoms for years. That's why regular check-ups are important; they can catch issues before they become serious.
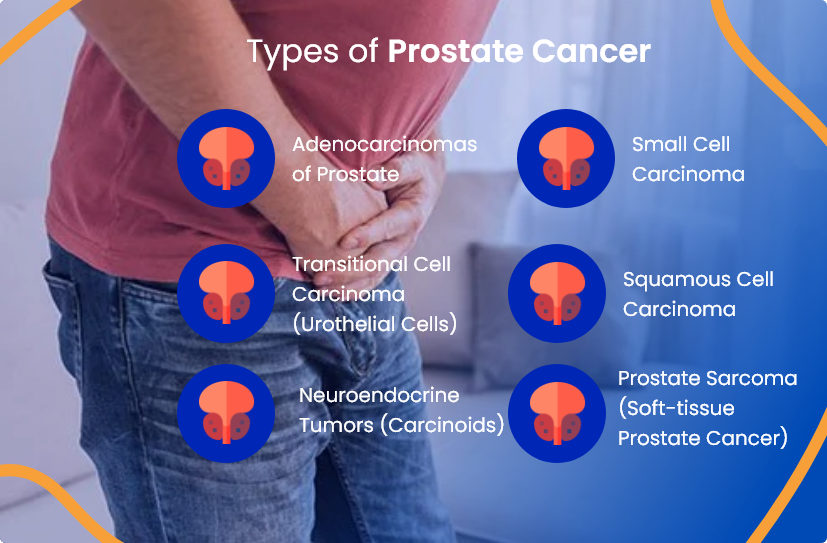
Nearly all prostate cancer cases—more than 95%—are adenocarcinomas.
Adenocarcinoma starts in the cells lining the prostate gland. There are two main subtypes:
Acinar adenocarcinoma (the most common): It typically grows at the back of the prostate, near the rectum. This location makes it easier for doctors to detect during a digital rectal exam (DRE). It also usually causes PSA (prostate-specific antigen) levels to rise in blood tests.
Prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A less common type that's often harder to detect early because it might not raise PSA levels as noticeably. It grows in the ducts and tubes inside the prostate and can be more aggressive.
Other types of prostate cancer are less common and don't typically raise PSA. These include:
Small cell carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma, prostate sarcoma (soft-tissue cancer)
Transitional cell carcinoma (originating from the bladder or urethra)
Neuroendocrine tumors
Prostate cancer usually doesn't cause symptoms early on. However, advanced prostate cancer can cause:
Difficulty urinating, such as weak or slow urine flow, or frequent urination, especially at night.
Blood appearing in urine or semen.
Burning sensation or pain during urination or ejaculation.
Pain in the back, hips, or chest if cancer has spread.
If you notice these symptoms, it's important to talk with your doctor.
If your doctor suspects prostate cancer, they will typically use a series of tests:
Digital rectal exam (DRE): The doctor gently inserts a lubricated, gloved finger into the rectum to feel the prostate for lumps or abnormalities.
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test: Measures a protein made by the prostate gland. Higher-than-normal levels might mean cancer, but can also indicate benign conditions.

Biopsy: The only definitive way to confirm prostate cancer. A small tissue sample from the prostate is examined under a microscope.
Transrectal ultrasound (TRUS): A small ultrasound probe is gently placed in the rectum to make clear pictures of the prostate using harmless sound waves. These images guide the doctor during a biopsy.

Your doctor will explain each step, ensuring you're comfortable and informed about what's happening and why.
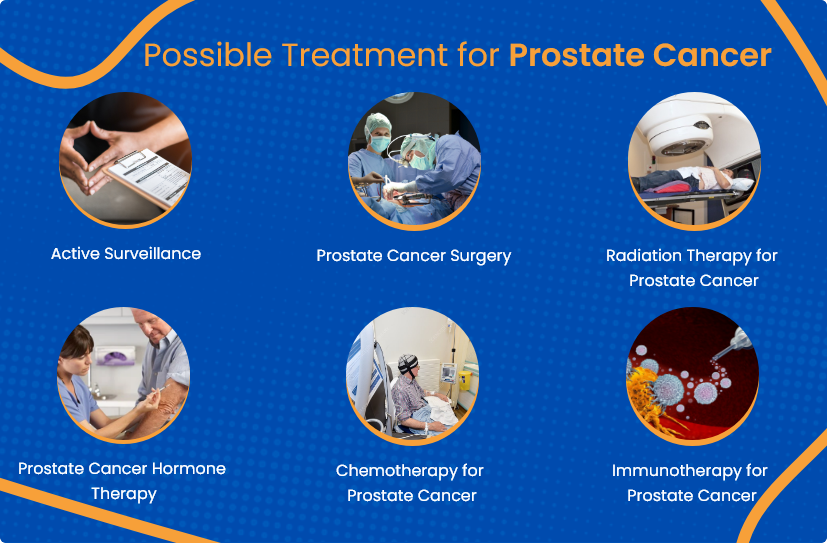
Prostate cancer treatment is tailored to each person based on the cancer’s stage, growth rate, and your overall health.
For low-risk, slow-growing cancers, your doctor may suggest active surveillance. This approach means regular check-ups, PSA tests, and biopsies to closely monitor the cancer and treat it only if it begins to grow.
Other common treatment options include:
Surgery: Radical prostatectomy removes the prostate and may include removing nearby lymph nodes.
Radiation therapy: This is a common treatment option, which can be given externally or internally by implanting small radioactive seeds.
Hormone therapy: This reduces male hormone levels that fuel cancer growth and is often used along with radiation therapy.
Chemotherapy: This uses anti-cancer drugs injected intravenously or administered orally, which then enter the bloodstream and reach and destroy rapidly growing cancer cells.
Immunotherapy: This is used to treat advanced prostate cancer and uses a specific protein to enhance the patient's immune system cells' ability to target and destroy abnormal cells.
Choosing a treatment plan is always a team effort between you and your healthcare providers, ensuring the decision matches your needs and preferences.
At ACTC, cancer care is personal. Our Florida-based specialists design evidence-based treatment plans tailored to each patient’s needs, with attention to both medical and emotional well-being. You’ll have a team by your side that treats you like family—because that’s how we define care.
You can consult with any of the following providers at ACTC:
At ACTC in Florida, our cancer specialists work closely with experienced clinical staff who’ve spent over 20 years supporting patients through every phase of care. From diagnosis to treatment and long-term follow-up, we provide expert guidance—all in one convenient location.
Call 352-345-4565 or book an appointment.

If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with prostate cancer, a frantic internet search for a ‘prostate cancer doctor near me’ may not be the best option. A detailed discussion with your primary physician would help you understand your condition better. Your pcp can then refer you to an advanced specialty center such as ACTC in Florida.
As one of Florida's advanced prostate cancer centers, we understand how a cancer diagnosis and therapy impact a person's physical and emotional well-being. Therefore, we work hard to make patients and their families feel secure. We understand that no two clinical cases are the same, and we strive to provide comprehensive treatment for all forms of prostate cancer at ACTC, staging, treatment, and long-term follow-up, all in one convenient location. Our prostate cancer specialists are backed up by qualified clinical staff with over two decades of experience and a reputation for providing personalized treatment.
Schedule a consultation by calling
 352-345-4565
352-345-4565
Factors that increase the risk of prostate cancer include: Increased age, African American ethnicity, family history of prostate cancer, obesity, and a diet high in saturated fats.
Yes. Many prostate cancers can be found early with a PSA blood test. A digital rectal exam (DRE) can sometimes find cancers even when PSA is normal. Because the benefits and risks of screening vary by age and personal risk, it’s best to decide on screening timing with your clinician.
Side effects depend on the treatment. Common ones include urinary leakage, trouble with erections/sex, and bowel changes. Not everyone has these; many can be managed or improved over time. Ask your care team how side effects are prevented and treated.
There’s no sure way to prevent prostate cancer. Healthy habits may help lower overall cancer risk: keep a healthy weight, be physically active, and build meals around vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting highly processed foods and sugary drinks. Discuss screening timing with your doctor if you have a higher risk.
Schedule a consultation by calling
 352-345-4565
352-345-4565