
Book a Consultation
Thank you!
Your form has been sent successfully.

A brain tumor occurs when brain cells multiply and grow uncontrollably, resulting in the creation of an abnormal mass of tissue. These tumors may be malignant or noncancerous (benign). Since the brain controls the body's vital functions, including speech, vision, movement, and thoughts, this cancer can significantly affect the quality of daily life, including altered speech, balance, thoughts, and personality.
The World Health Organization classifies brain tumors according to the origin of the cells, and they can range from least aggressive (benign) to most aggressive (malignant). Brain cancers can be divided into primary and secondary types.
It originates in the brain or central nervous system. According to the National Brain Tumor Society, there are more than 120 types of brain and central nervous system tumors. Some of the most common primary brain tumors, according to the origin of the cells, are:
Gliomas, which arise in glial cells, cause about 3 out of 10 cases of brain cancer. Among gliomas types, astrocytoma is the fastest-growing brain cancer. Other types of gliomas tumors include oligodendrogliomas and glioblastomas.
Meningioma grows from cells that surround the brain and spinal cord. According to National Cancer Institute, meningioma is the most common primary brain tumor.
Ganglioglioma is a type of tumor that grows slowly in neurons and glial cells and is usually treated with surgery.
Craniopharyngioma tumor grows slowly in between the pituitary gland and brain. It usually impinges on the optic nerve causing vision difficulties.
During fetal growth, germ cells help form different parts of the body. However, if germ cells migrate to the brain, they can develop into tumors. Some germ cell tumors are yolk sac tumors, teratomas, germinomas, and embryonal carcinomas.
Pineal tumors develop in the deep areas of the pineal gland region. Pineal tumors may block the cerebrospinal fluid and cause hydrocephalus. Various types of pineal tumors are pineal parenchymal tumors of intermediate differentiation, pineocytomas, and pineoblastoma.
It occurs when cancer originates in other areas of the body, spreads to the brain, and is more common than primary brain cancer. Cancer of the lungs, colon, kidney, and breast can spread to the brain. The prognosis for metastatic brain cancer depends on the growth rate of cancerous cells. Some common secondary brain tumors are:
Lymphoma develops from the lymphatic system (part of the immune system) and can spread from other body parts to the brain. Primary lymphoma brain cancer starts in white blood cells in the brain.
Melanoma starts in the melanin cells of the skin and spreads rapidly via lymph nodes to the brain, which is called melanoma brain cancer.
According to research, medulloblastoma is the most common malignant brain tumor found in children under 15 years of age. It grows at the base of the skull, and the growth rate depends on the mutation of tumor cells.
It is an aggressive type of bone cancer that arises from the cartilage of the spine, skull base, pelvis, arm, knee, and thighbone - that can reach the brain.
Brain cancer symptoms vary according to the location of the tumor and the functional system impacted. Common signs and symptoms of brain tumors may include:
 Headaches that worsen with time
Headaches that worsen with time
 Unexplained nausea and vomiting
Unexplained nausea and vomiting
 Double or blurred vision or loss of peripheral vision
Double or blurred vision or loss of peripheral vision
 Memory loss and confusion
Memory loss and confusion
 Muscle weakness and difficulty with balance along with involuntary jerks or twitching of muscle
Muscle weakness and difficulty with balance along with involuntary jerks or twitching of muscle
 Episodes of a sudden loss of consciousness
Episodes of a sudden loss of consciousness
 Numbness in extremities
Numbness in extremities
 Unexplained seizures
Unexplained seizures
 Hearing problems
Hearing problems
 Difficulty in speech
Difficulty in speech
 Tiredness and drowsiness
Tiredness and drowsiness
Brain cancer treatment options depend upon the size, location, and type of tumor. Age and overall health are also considered before deciding on an optimum treatment for brain cancer cure.
Surgical procedures are the most common brain cancer treatment options. The procedure depends on the tumor's size, location, and accessibility. There are many surgical approaches for the removal of a brain tumor:
Craniotomy: A craniotomy is a surgery where a skull piece is temporarily removed to allow surgeons access to the brain.
Awake brain tumor surgery: When a tumor is adjacent to vital structures like nerves, then patients are sedated but kept awake during surgery so surgeons can confirm that normal brain functions are not affected.
Neuroendscopy: To minimize scarring and for better reach in some regions of the brain, surgeons use other parts of the body (such as the nose) to enter the brain.
Neuroplastic surgery: After invasive procedures, the neurosurgical approach repairs and maintains the skull's appearance and anatomy.
MRI-Guided Laser Ablation Laser and Interstitial Thermal Therapy: It is a minimally invasive procedure where computer imaging locates the tumor. Then cancerous cells are precisely focused on and destroyed with heat or lasers.
Radiation for brain cancer uses high ionizing rays to destroy cancer cells that are otherwise inaccessible by surgery.
External beam radiation treatment for brain cancer: It is the most common usage of radiotherapy for this type of tumor, where the tumor and nearby tissues or the entire brain are exposed to high-intensity radiation. Whole-brain irradiations treat metastatic brain cancer when multiple small metastatic foci are spread across the brain.
Stereotactic radiosurgery: Small and more focused X-ray beams are used to target and destroy the tumor cells while sparing healthy surrounding tissue. It is often used to treat inaccessible brain tumors.
Chemotherapy (chemo) for brain cancer is a treatment that uses medicines to kill cancer cells and is often used along with surgery and radiotherapy. Surgeons may surgically implant chemotherapy drugs in the form of wafers to bypass the blood-brain barrier and deliver the drug specifically to areas in the brain affected by cancer.
Targeted drug therapy explicitly targets specific cell proteins that stop cancer growth. It causes fewer side effects as it spares healthy cells because of its specific action. It is often combined with radiotherapy and surgery to treat metastatic brain cancer.
Tumor-treating field sends painless electrical impulses on the skin of the scalp to disrupt the division of tumor cells. It acts on specific cell proteins required for cell division and tumor growth. The portable device with a small backpack is continuously used by the patient while carrying out their daily activities.
The following tests and procedures may be recommended if your doctor suspects that you have a brain tumor:

It includes checking the various functions like sight, hearing, reflexes, balance, and coordination. Abnormality in one or many functions may suggest which areas of the brain are affected by the tumor.
MRI is a common procedure to diagnose brain tumors. Functional MRI, perfusion MRI, and magnetic spectroscopy are various types of MRI that help specialists diagnose and plan treatment. Other imaging techniques like computerized tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) can also locate the brain tumor.
CT or MRI scans usually guide stereotactic needle biopsy to reach inaccessible brain areas. A surgeon drills a small hole in the skull and inserts a needle to remove the tissue, which is later microscopically investigated for brain cancer.
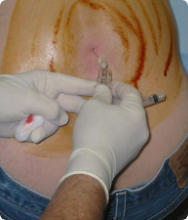
A lumbar puncture is a procedure where a sample of the fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord is removed by inserting a hollow needle in the lower back to diagnose the presence of cancer cells.
The brain cancer specialists at ACTC, Florida, offer outstanding patient care by prescribing personalized and evidence-based treatment plans tailored to individual patients' needs. We aim to foster a positive environment that focuses on physical and mental health throughout a cancer patient's journey.
The following are our providers who you can consult at ACTC:

Hematology/Oncology

Hematology/Oncology

Radiation Oncology

If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with brain cancer, having a detailed discussion with your primary physician will help you understand your condition better and get a referral to an advanced specialty center such as ACTC in Florida.
As one of Florida's best brain cancer centers, we understand how a cancer diagnosis and therapy impact a person's physical and emotional well-being. Therefore, we work hard to make patients and their families feel secure. We understand that no two clinical cases are the same, and we strive to provide comprehensive treatment for all forms of brain cancer at ACTC– staging, treatment, and long-term follow-up, all in one convenient location. Our cancer specialists are backed up by qualified clinical staff with over two decades of experience and a reputation for providing personalized brain cancer treatment.
Schedule a consultation by calling
 352-345-4565
352-345-4565
Benign tumors grow slowly and can be safely monitored by doctors for months or years. Many malignant tumors are aggressive and fast-growing and require immediate intervention.
According to the American Cancer Society, apart from certain lifestyle changes like reducing contact with carcinogens and radiation exposure, no known steps can be taken to prevent brain cancer.
If you are based in (or near) Florida, you can schedule a consultation with an ACTC cancer specialist by calling 352-345-4565 or completing the online form at www.actchealth.com
Schedule a consultation by calling
 352-345-4565
352-345-4565