
Book a Consultation
Thank you!
Your form has been sent successfully.

A form of cancer known as Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma develops in the lymphatic system, which is a component of the body's immune system that fights infection. White blood cells called lymphocytes can develop tumors (growths) throughout the body when Non-Lymphoma Hodgkin's is present. It is the seventh most common form of cancer in the US.
The majority of NHL (Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma) subtypes fall into one of two categories:
Here are the most common types of NHL:
It is a type of blood and bone marrow cancer called chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) that affects the spongy tissue inside bones where blood cells are created.
White blood cells give rise to a rare form of cancer called cutaneous B-cell lymphoma. This malignancy targets the skin. One type of white blood cell known as B cells, which fights infection, is where cutaneous B-cell lymphoma develops.
An uncommon form of cancer known as cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) starts in T cells, which are white blood cells (T lymphocytes). Normally, these cells support the body's immune system in battling infections.
When the body produces B cells that aren't normal, follicular lymphoma forms. These lymphocytes are a category of white blood cell that typically aids in the defense against infections. The abnormal lymphocytes accumulate in the lymph nodes or other body organs when lymphoma is present.
This is a kind of lymphoma that affects the bone marrow and lymphatic tissues and is defined by the presence of unusually high numbers of B lymphocytes, a specific type of white blood cell. The body produces abnormal amounts of the antibody protein IgM when these cells build up. Some of the symptoms of the illness are brought on by high levels of IgM, which thicken the blood (hyperviscosity) and impair the blood flow through the smaller blood vessels.
 Chest pain
Chest pain
 Rough skin
Rough skin
 Reduced appetite
Reduced appetite
 Cough
Cough
 Trouble breathing
Trouble breathing
 Enlarged lymph node
Enlarged lymph node
 Fatigue
Fatigue
 Fever
Fever
 Night sweats
Night sweats
 Unexplained weight loss
Unexplained weight loss
Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma treatment depends on the specifics of the lymphoma, such as the types of cells involved and whether the lymphoma is aggressive. Doctors will choose the appropriate treatment or combination of treatments accordingly.
It is a medication used to treat cancer that can be administered intravenously or orally. Medications used in chemotherapy can be used individually, in conjunction with other drugs or therapies. Chemotherapy is also a component of bone marrow transplants, commonly known as stem cell transplants, for patients with Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma. Chemotherapy in high doses can also be used to eliminate the abnormal stem cells, blood cells, and cancer cells - thus preparing the body for the upcoming transplant.
High-powered energy beams, such as x-rays and protons, are used in radiation therapy to destroy cancer cells. Radiation therapy may be the only option for treating Non-Hodgkin's disease, especially if the tumors are slow-growing and limited to one or two sites in the body. Radiation is typically administered following chemotherapy to eliminate any remaining lymphoma cells. One option is to aim radiation at the afflicted lymph nodes and surrounding nodes where the disease may spread.
These therapies concentrate on particular defects that are prevalent in cancer cells. Targeted medication therapies can kill cancer cells by preventing these abnormalities. Chemotherapy is used in combination with targeted medications to treat Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma. If the lymphoma recurs, doctors can use this combination as the initial treatment and as a follow-up.
Immunotherapy is a form of cancer treatment that either works to strengthen the patient's own immune system or uses artificial versions of immune system components to either kill or suppress lymphoma cells.
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy is a specialist procedure that employs the body's immune system's T cells to attack cancer. For some B-cell non-lymphomas Hodgkin's that have not responded to conventional therapies, CAR-T cell therapy may be an alternative form of therapy.
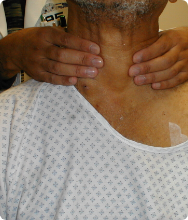
The doctor examines the spleen, liver, and lymph nodes in the neck, underarms, and groin for swelling.
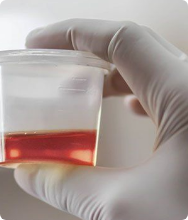
Blood and urine testing is used to rule out infections and other diseases.

In order to detect lymphoma cells elsewhere in the body, the doctor may recommend imaging tests. CT, MRI, and positron emission tomography are a few possible tests (PET).

To remove all or part of a lymph node for laboratory testing, the doctor may advise a lymph node biopsy surgery.
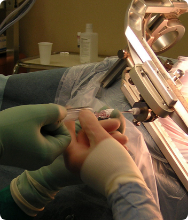
The doctor may take a sample of the lymph node for testing during a biopsy. This will enable the diagnosis of NHL (Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma). The doctor may further perform a bone marrow biopsy to assess whether the illness has spread.
Our patients have access to a multispecialty team of professionals at ACTC, who work together in a highly collaborative and coordinated manner to provide all aspects of cancer care in one convenient location in Brooksville, Florida. Our doctors are supported by a clinical team with over two decades of experience and a reputation for providing customized and supportive cancer care.
The following are our providers who you can consult at ACTC:

MD, Hematology & Oncology

MD, Ph.D., Hematology/ Medical Oncology

MD, Radiation Oncologist

If diagnosed with Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma cancer, you may face a series of hard choices. Our experts at ACTC will guide you and your family through every step of cancer treatment. With state-of-the-art technology and experienced cancer specialists, ACTC promises its patients world-class healthcare.
Schedule a consultation by calling
 352-345-4565
352-345-4565
The Lugano classification is the current staging scheme for NHL in adults. Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma stages are denoted through roman numerals I through IV.
Low-grade disorders start to rapidly progress after five to ten years, at which point they turn aggressive or high-grade and exhibit more severe symptoms. This kind of NHL advances rather quickly - especially in the absence of treatment.
Although the precise reason for the occurrence of this disease is unknown, Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma is brought on by a change (mutation) in the DNA of a type of white blood cell called lymphocytes.
Schedule a consultation by calling
 352-345-4565
352-345-4565