
Book a Consultation
Thank you!
Your form has been sent successfully.

A pituitary gland tumor develops as an abnormal growth in the pituitary gland. This kind of pituitary tumor can either lead to excessive production of hormones or a deficiency which in turn can lead to hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, fatigue, muscle weakness, and more. As per research conducted by the American Cancer Society, approximately 10,000 pituitary gland tumor cases are recorded in the US every year. Generally, these are benign (non-cancerous) and only a few are cancerous.
The different types of pituitary gland tumors are:
These usually affects women more than men and produce increased levels of prolactin in the body. In women, a high level of prolactin can lead to irregular menstruation or even stop it. Even if the individual is not pregnant, the person can produce breast milk. Men with prolactin-producing tumors can suffer from erectile dysfunction or have a low sperm count.
These are the most common type of pituitary gland tumor. Unlike the other types, non-functional adenomas do not produce any additional hormones. When the mass increases in size, it can cause vision problems and headaches.
An increased level of growth hormone is released by this type of tumor. When this happens, it results in the growth of the bones in the body, leading to a condition called acromegaly. It is characterized by joint pain, widely spaced teeth due to the growth of facial bones, and deepened voice.
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) triggers the adrenal gland to produce steroids (glucocorticoids) that impact metabolism. Excessive ACTH levels can lead to Cushing’s disease, which may be evident from extra fat deposits, muscular weakness, hair loss, insomnia, excessive hunger, and more.
People with a pituitary tumor can display any of the following symptoms:
 Nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting
 Mood swings
Mood swings
 Headaches
Headaches
 A feeling of exhaustion without reason
A feeling of exhaustion without reason
 Infertility
Infertility
 Erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction
 Irregular menstrual cycles
Irregular menstrual cycles
Doctors can determine the best course of treatment for this condition after considering factors like age, type of tumor, overall health condition and more. Treatment options for pituitary tumors include:
In most cases, a pituitary tumor must be surgically removed if it presses on the optic nerves or if it produces too much hormone. A tumor's size, location, and degree of invasion of nearby tissues determine if the patient should undergo a surgery.
In radiation therapy, high-energy beams target and destroy the cancer cells in the affected area. Radiation therapy is also prescribed if the tumor persists or returns following surgery and causes symptoms that medications cannot alleviate.
In this treatment method, the doctor prescribes certain medications to prevent a pituitary tumor from producing excessive hormones.
This treatment is suggested if the pituitary gland is not producing the required hormone sufficiently due to the presence of the tumor. Hormones administered for replacement include thyroid, growth, estrogen, testosterone, and other hormones.
Doctors can recommend any of the following tests to diagnose a pituitary tumor:
A CT scan (computed tomography) or an MRI enables a doctor to determine the size and location of the pituitary tumor.
These tests are done to check the levels of various hormones in a patient’s urine and blood.
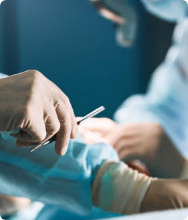
In this test, a small sample of tissue is removed from the affected region. The sample is evaluated under a microscope to check for the presence of cancer and other irregularities occurring in the cells.
The specialists for pituitary gland tumors at ACTC in Florida, offer outstanding patient care by prescribing personalized and evidence-based treatment plans tailored to individual patients' needs. We aim to foster a positive environment that focuses on physical and mental health throughout a cancer patient's journey.
Consult with the following physicians at ACTC:

MD, Hematology & Oncology

MD, Ph.D., Hematology/ Medical Oncology

MD, Radiation Oncologist

As one of Florida's leading advanced pituitary gland tumor treatment centers, we understand how a cancer diagnosis and treatment impact a person's physical and emotional well-being. Therefore, we work hard to make patients with all forms of cancer and their families feel secure. We provide comprehensive treatment for carcinoid tumors at ACTC, including screening, diagnosis, staging, treatment, and long-term follow-up, all in one convenient location. Our physicians are backed up by qualified clinical staff with over two decades of experience and a reputation for providing individualized treatment.
Schedule a consultation by calling
 352-345-4565
352-345-4565
Tumors of this type are not usually cancerous. It is extremely rare for pituitary cancer to develop. However, tumors can cause serious problems, either producing higher or lower levels of hormones that can affect the body's functioning. They can be usually treated with medication, surgery, or radiation.
A tumor in the pituitary area may lead to an increased or decreased production of hormones, altering the normal functions of the body. If the pituitary gland is secreting too many hormones, it will prompt the other glands to do the same. Pituitary tumors are usually benign (noncancerous) and do not spread to other body parts.
Pituitary tumors occur in the pituitary gland, which lies beneath the brain and behind the eyes on the inside of the skull. Pituitary tumors are not brain tumors, and the pituitary area is not a part of the brain.
Schedule a consultation by calling
 352-345-4565
352-345-4565