
Book a Consultation
Thank you!
Your form has been sent successfully.



March 09, 2023
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma (ACC) is a rare type of cancer that starts from the cells of the glands and ducts in the body, such as the salivary glands, lacrimal glands, or breast ducts. ACC is considered slow-growing, which means it can take several years to grow and spread. However, it can also be quite invasive, and sometimes, it can spread to the lymph nodes, bones, or other organs.
ACC is most found in the salivary glands, with most cases that accounts for around 70% cases, originating in the parotid gland. The exact cause of this cancer is not known, but researchers believe it may be related to genetic mutations or changes in certain genes. Let’s look at the primary causes and risk factors and symptoms of Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma.
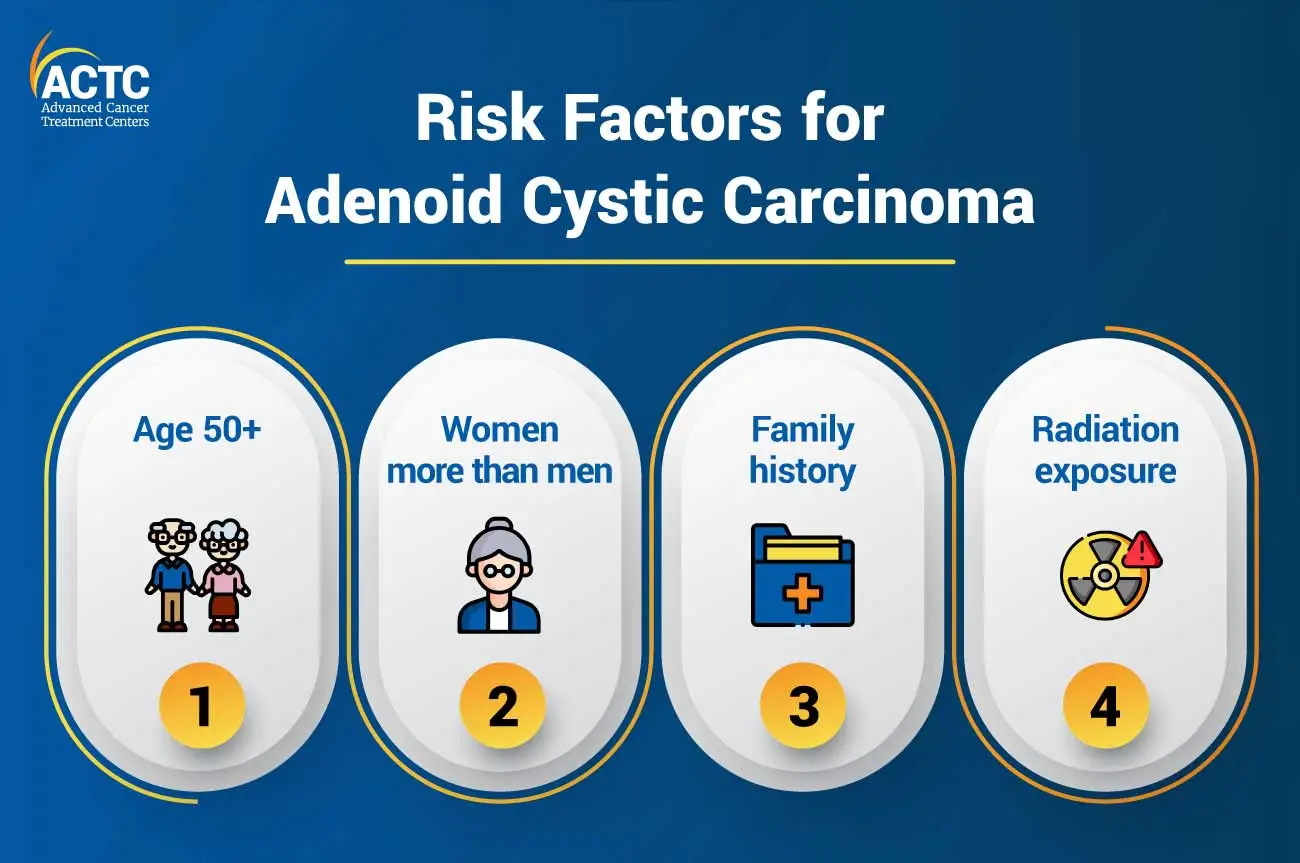
The most common cause of ACC is a genetic mutation in the tumor cells that leads to uncontrolled growth and proliferation. However, ACC is considered to be a sporadic cancer, meaning that it occurs by chance rather than as a result of inherited genetic mutations or environmental exposures.
A few risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing ACC are as follows:
It is crucial to note that these risk factors do not necessarily mean that a person will develop ACC. Besides, many people with ACC may not have any of these risk factors.
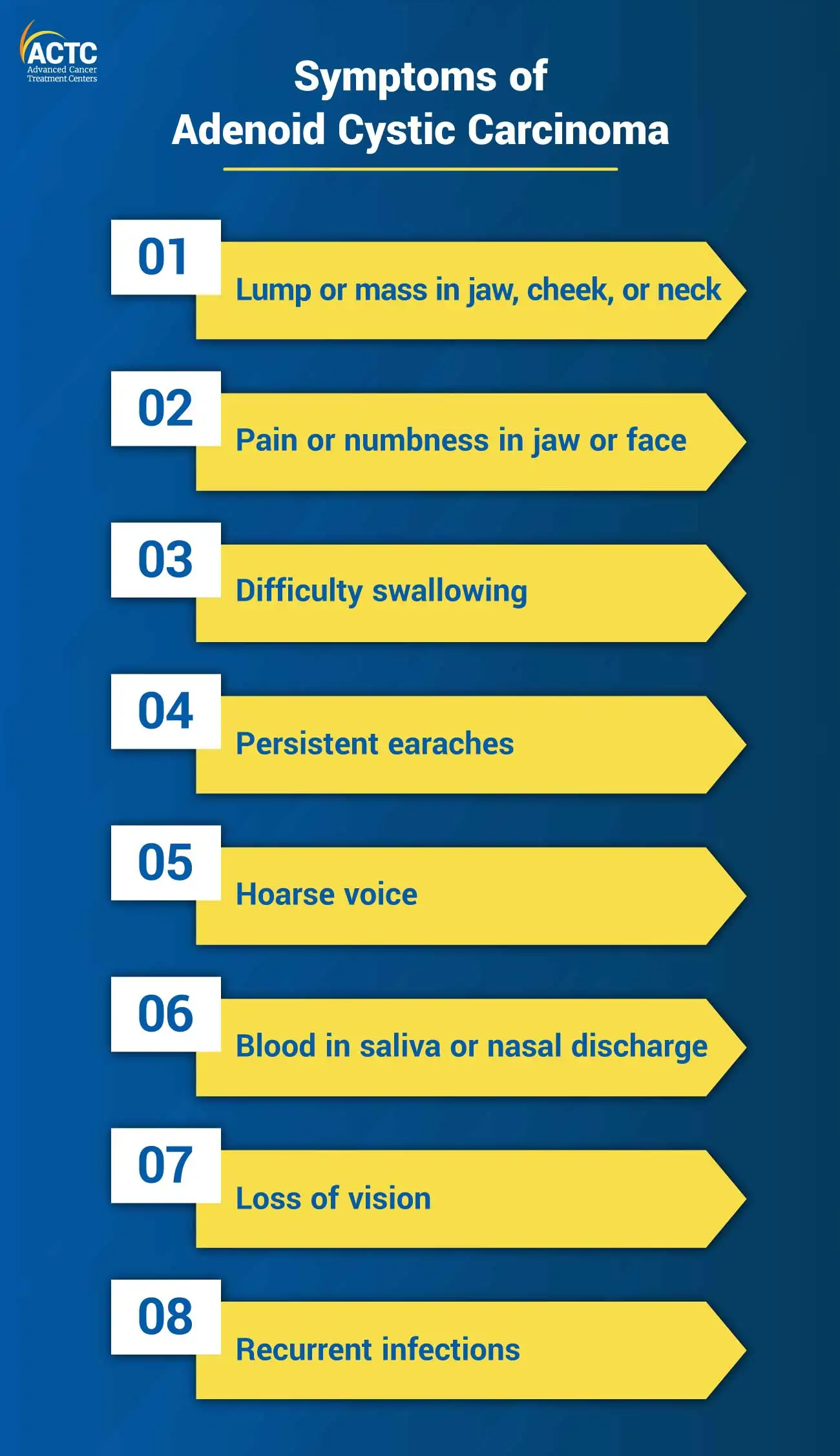
Adenoid cystic carcinoma symptoms can vary depending on the location of the tumor, but some common symptoms are as follows:
These symptoms can also be caused by other conditions and do not necessarily indicate ACC. If a person experience any of these symptoms, consult with a healthcare professional at the earliest for proper diagnosis and treatment.
The treatment procedure depends on the size, location, and stage of the tumor, as well as the overall health of the patient. The main treatment options for ACC include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy.
It is the most common treatment for ACC, especially for tumors that are localized to one area. The goal of surgery is to remove the tumor and any surrounding tissue where the cancer may have spread. Depending on the location of the tumor, there are different types of surgery which are as follows:
It uses high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells and shrink tumors and often used in conjunction with surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence. Radiation therapy can also be used as a primary treatment for patients unable to undergo surgery due to their age or other medical conditions.
With chemotherapy, doctors administer drugs orally, intravenously or in a combination of to kill cancer cells. It is often used with radiation therapy but can also be used as a primary treatment for patients with advanced or recurrent ACC.
It is a newer type of cancer treatment that targets specific molecules or pathways involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells. Some examples of targeted therapies used in the treatment of ACC include EZH2 inhibitors, Hedgehog pathway inhibitors, and PI3K inhibitors.
The treatment plan for ACC is typically determined by a team of healthcare professionals and it is tailored to each individual patient. The healthcare team takes the stage and location of the tumor, as well as the patient's overall health and treatment preferences into consideration while deciding the treatment plan.
The 5-year relative survival rate for ACC is around 65% to 70% which means around 65% to 70% of people with ACC are expected to live at least 5 years after their diagnosis. However, survival rates can vary depending on the stage of the cancer at the time of diagnosis.
For instance, the 5-year relative survival rate for localized ACC or cancer that has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant organs is around 90%. But the same for metastatic ACC is around 20%.
The risk of recurrence for ACC is relatively high, with around 30-50% of patients experiencing a recurrence of the cancer even after successful treatment. The risk of recurrence is higher for patients with advanced stage ACC, and for people who have not undergone complete surgical resection of the tumor.
Coping with ACC diagnosis can be difficult, and it is important to find ways to manage stress and anxiety. Talk to a therapist, join a support group, practice relaxation techniques such as yoga or meditation, and connect with friends and loved ones. Also, make healthy lifestyle choices to improve overall health and well-being during and after treatment. To receive the best cancer care for Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma, contact ACTC and schedule an appointment.



January 07, 2026
A chemo port is a small device placed under your skin that makes recei...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
It's natural to wonder if testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is sa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A rash that will not calm down is scary, especially when it changes or...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Florida’s lung cancer burden remains significant and affects many fa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A partial hysterectomy, also called a supracervical hysterectomy, is s...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Finding a rash on your breast can be unsettling, but remember, many ra...
KNOW MORE
