
Book a Consultation
Thank you!
Your form has been sent successfully.



January 11, 2022
In the United States, cancer is one of the leading causes of death every year. According to the American Cancer Society, around 1.8 million new cancer cases were diagnosed in 2020, with approximately 606,520 deaths taking place.
Cancer is a condition in which some cells grow abnormally, divide quickly, and spread to other parts of the body. It can begin practically anywhere in the trillions of cells that make up the human body. According to the National Cancer Institute, there are over 100 malignancies that originate from various cell types, and these malignancies are found in different body organs. Research is still being done to help comprehend and treat these varied conditions.
Cancer treatment and medications have evolved, as time and technology have progressed. In recent years, we've seen various approaches that work to enable healing. One such approach today is personalized cancer treatment. Let us delve deeper into its details:
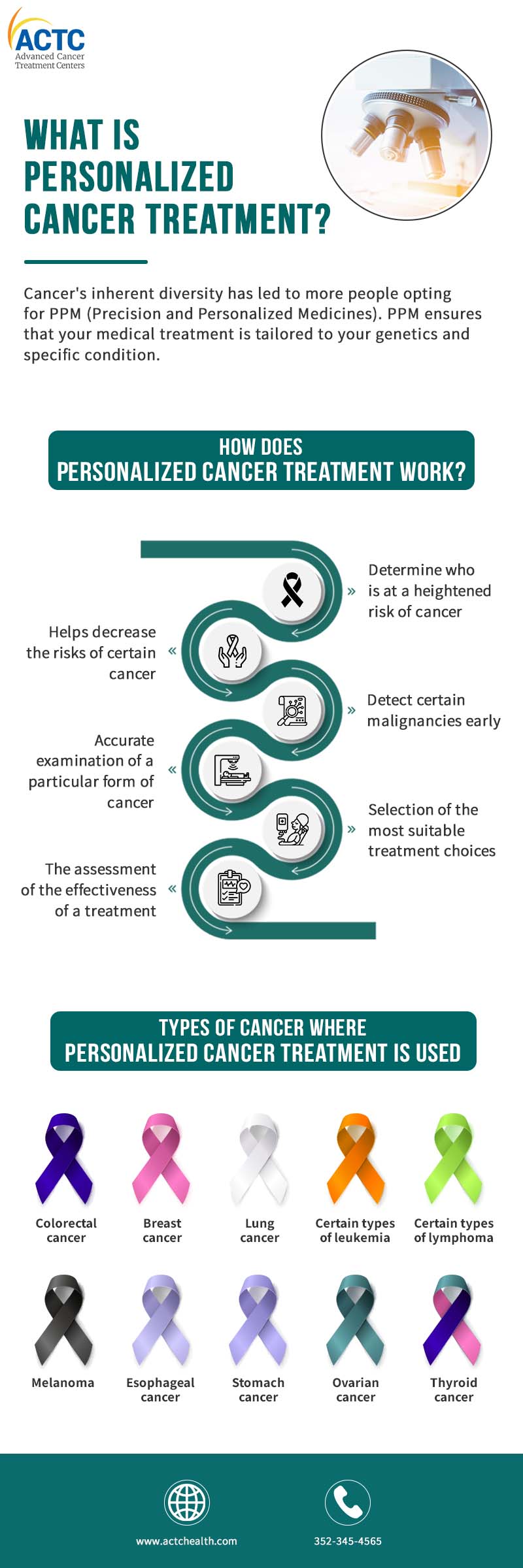
Cancer may have a variety of inherited causes. Over the last decade, it has been increasingly obvious that no two individuals' cancers are precisely the same, and even generic therapies like chemotherapy and radiation may have varying outcomes. The inherent diversity of this disease has led to more people opting for PPM (Precision and Personalized Medicines), and this trend is steadily increasing.
PPM ensures that your medical treatment is tailored to your genetics and specific condition. Genes are instructions that tell your body's cells how to improve and evolve. Many cancers are linked to or affected by individual genes. Personalized Medicine studies how a certain gene mutation may influence a person's risk of developing this disease. It can also reveal how their genes may influence the treatment process if they already have the disease.
Genetic tests are used to assist doctors in creating a treatment plan, which usually includes very specific recommendations.
Read more: 9 Thoughtful Gifts for Cancer Patients
Personalized cancer treatment is now being used to determine which tests and treatments are best for certain malignancies. With the use of personalized treatment, a doctor will be able to help patients in the following ways:
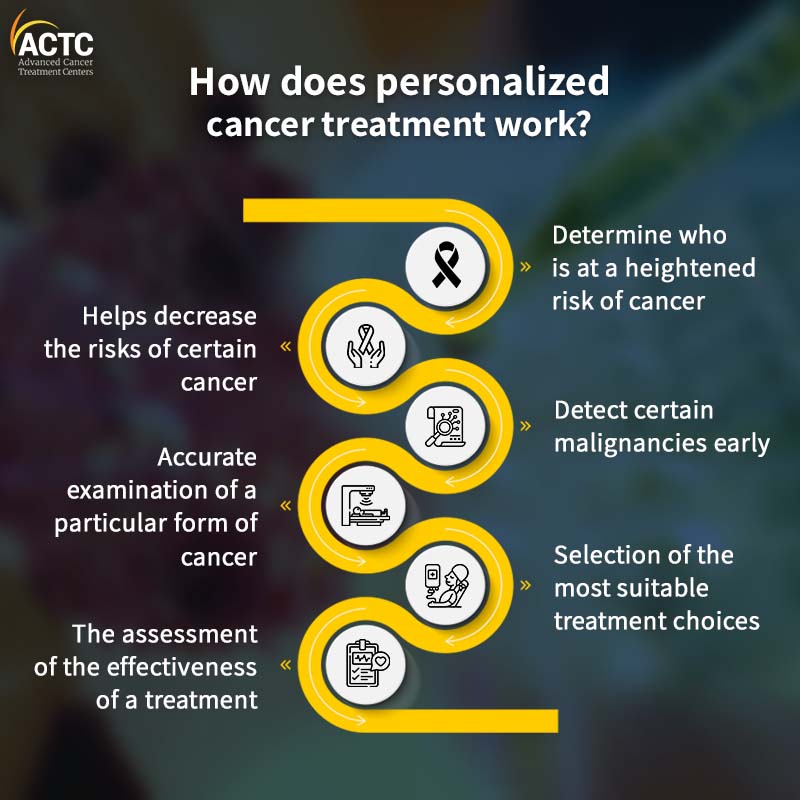
It's essential to recognize that precision medicine isn't used for every malignancy. However, it is hoped that one day, medicines will be tailored to each person's gene mutations in cancer. Many studies are being conducted for this.
The following are amongst the most common malignancies for which personalized treatment is being used:
Certain types of leukemia
Certain types of lymphoma
Esophageal cancer
Stomach cancer
Thyroid cancer
Many medical trials enlist patients with certain cancer types at different stages. To participate in a personalized medicine clinical study, a person must have a specific genetic mutation that the medication can address. Drug trials in personalized medicine are generally only available at larger cancer centers.
The precision and personalized medicines treatment approach has expanded and matured a lot in recent years. This data has been linked to individual case results and research responses that have moved beyond exact sequencing.
Studies suggest that the personalized technique has surpassed the usual approach by 30.6 percent versus 4.9 percent in cancer patients. These figures show that the reaction of patients significantly improves when they receive customized treatments for their specific condition. Overall, PPM's premise is intriguing and encouraging, and it has the potential to revolutionize cancer treatment.


January 07, 2026
A chemo port is a small device placed under your skin that makes recei...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
It's natural to wonder if testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is sa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A rash that will not calm down is scary, especially when it changes or...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Florida’s lung cancer burden remains significant and affects many fa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A partial hysterectomy, also called a supracervical hysterectomy, is s...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Finding a rash on your breast can be unsettling, but remember, many ra...
KNOW MORE
