
Book a Consultation
Thank you!
Your form has been sent successfully.



August 28, 2023
Immunotherapy uses the power of the body's natural immune system to recognize and eliminate cancer-affected cells. While immunotherapy has revolutionized cancer treatment, it may also trigger a range of side effects, which can vary in intensity and manifestation depending on a person’s health condition and the spread of cancer.
In this blog post, we will share a comprehensive understanding of why immunotherapy causes side effects, what the side effects are and what individuals can do to manage them efficiently. Read on to learn more.
There are several types of immunotherapy used in cancer treatment, and each type can cause side effects due to their specific mechanisms of action. The following are the primary reasons why immunotherapy can cause side effects:
Immunotherapy drugs, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, work by blocking proteins that act as "brakes" in the immune system. By removing these brakes, immunotherapy boosts the immune system's ability to attack cancer cells. However, this heightened immune response can sometimes become overactive and attack healthy cells and tissues as well, resulting in side effects.
Inflammation is a normal immune process that helps the body fight off infections and heal wounds. However, immunotherapy can trigger chronic inflammation, which can cause discomfort and damage to healthy tissues. In can eventually result in a number of side effects.
Each person's immune system works in a unique way, and individual responses to immunotherapy can vary. Factors such as genetic makeup, overall health, and prior treatments can influence the occurrence and severity of side effects. Some individuals may experience minimal side effects, while others may experience more pronounced or severe reactions.
The side effects of immunotherapy can range from mild to severe and individuals should discuss their risk with their cancer care team to consider the treatment option carefully.
The occurrence of side effects from immunotherapy treatment can vary among individuals. While some people may not experience any side effects, approximately 20% of those receiving immunotherapy may encounter an immune-related adverse event (irAE). The likelihood of experiencing side effects may be higher for individuals receiving a combination of immunotherapy drugs, a combination of different cancer treatment procedures like chemotherapy, radiotherapy, etc., or those with a pre-existing autoimmune disease.
Fortunately, most side effects are mild in nature and can be effectively managed through some measures.

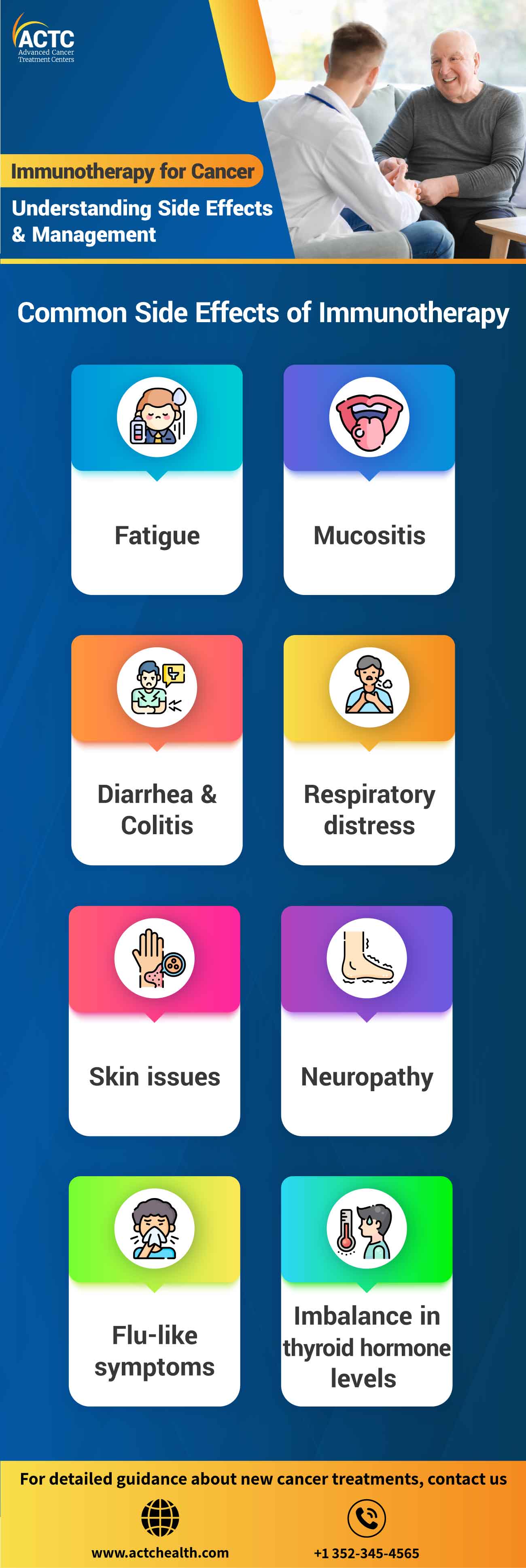
It is a common side effect of immunotherapy characterized by extreme tiredness, lack of energy, and difficulty performing daily activities.
Prioritize rest and ensure adequate sleep.
Maintain a healthy balance between physical activity and rest periods to conserve energy.
Engage in light exercise or physical activity, if permitted by a healthcare provider.
Read more: A Complete Guide to Exercise During Cancer Treatment
Immunotherapy can cause inflammation in the digestive tract and produce side effects such as frequent loose or watery bowel movements, abdominal pain, cramping, and sometimes blood in the stool.
Prevent dehydration by drinking plenty of fluids.
Eat low-fiber and non-spicy foods to reduce irritation to the digestive tract.
Inform your healthcare team about the frequency, consistency, and severity of diarrhea to determine appropriate interventions.
Healthcare providers may prescribe certain medications, such as antidiarrheals or corticosteroids, to manage digestive issues caused by immunotherapy.
It refers to inflammation and ulceration of the mucous membranes, commonly affecting the mouth and throat. It can cause pain, difficulty swallowing, and mouth sores.
Maintain good oral hygiene with gentle brushing and rinsing using non-irritating mouthwashes.
Avoid hot or spicy foods and acidic or rough-textured foods.
Opt for softer or liquid foods if swallowing becomes difficult.
Stay hydrated and use oral moisturizers as recommended.
Immunotherapy can exhibit signs of respiratory issues such as coughing, shortness of breath, or lung inflammation (pneumonitis).
Avoid exposure to respiratory irritants, such as smoke or pollution.
Notify the healthcare team immediately if you experience any respiratory symptoms.
Follow the healthcare provider's recommendations regarding further evaluation, such as chest imaging or pulmonary function tests.
Doctors may prescribe medications such as corticosteroids, may be prescribed to manage lung inflammation.

Immunotherapy can cause various skin reactions, including rashes, itching, dryness, blistering, or changes in pigmentation.
Keep the skin clean and moisturized.
Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures, harsh chemicals, or irritants.
Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing.
Use topical corticosteroids or other prescribed creams to avoid dry skin or irritation.
Apply sunscreen at frequent intervals, especially when outdoors, to avoid any damage from UV rays.
Read more: 5 Ways to Protect Your Skin From UV Rays
It refers to nerve damage that can cause symptoms like tingling, numbness, weakness, or pain, often in the hands and feet.
Practice good foot and hand care, including regular inspection and moisturization.
Protect hands and feet from extreme temperatures.
Report any neuropathy symptoms to your healthcare team promptly. They may recommend physical therapy or medications to manage neuropathic symptoms.
Immunotherapy can stimulate an immune response that mimics flu-like symptoms. including fever, chills, body aches, fatigue, and headaches.
Rest and stay hydrated.
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen, can help manage fever and body aches, but it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider before taking any medication.
Immunotherapy can cause changes in thyroid hormone levels, leading to either an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) or an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism). Symptoms of hormonal imbalance may include fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, and temperature intolerance.
Get routine tests and screenings done to monitor thyroid hormone levels.
Healthcare providers may prescribe medications such as thyroid hormone replacement or anti-thyroid medication to restore thyroid function.
In order to manage these side effects efficiently, individuals should communicate openly with their healthcare team. They can provide personalized guidance, monitor the side effects closely, and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan accordingly.
Read more: Making the Best of Life After Cancer
Like any medical intervention, immunotherapy also produces some side effects. The potential benefits of immunotherapy in combating cancer often outweigh the associated side effects. With ongoing research and advancements in supportive care, the medical community continues to refine strategies to minimize side effects and enhance the overall effectiveness and safety of immunotherapy.
For any queries or concerns about immunotherapy for cancer treatment, contact ACTC, one of the best cancer centers in Florida, offering personalized cancer care plans.


January 07, 2026
A chemo port is a small device placed under your skin that makes recei...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
It's natural to wonder if testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is sa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A rash that will not calm down is scary, especially when it changes or...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Florida’s lung cancer burden remains significant and affects many fa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A partial hysterectomy, also called a supracervical hysterectomy, is s...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Finding a rash on your breast can be unsettling, but remember, many ra...
KNOW MORE
