
Book a Consultation
Thank you!
Your form has been sent successfully.


December 30, 2021
Cancer has caused over 10 million deaths in 2020 - making it one of the leading causes of human mortality. Over time, several attempts have been made to find a cure for the disease. Since treatment protocols have limited efficiency in fighting cancer-causing cells, there has been a constant search for advanced procedures that can deliver improved outcomes. One such option is that of Immunotherapy - which utilizes and enhances the capacity of the patient's immune system and hence seems to be providing improved results.
The human immune system can be used to combat various infections and diseases. Our cells, organs, and body proteins are all considered to be part of it. Much of the immune system's natural protection is bypassed when cancer develops in the body, allowing cancerous cells to continue to grow.
In this situation, Immunotherapy is a solution that boosts the body's natural resistance and the ability to fight cancer. It improves how one's immune system discovers and destroys cancer by using molecules manufactured in one's own body or laboratories. Some immunotherapy treatment work by assisting the immune system in slowing or stopping cancer development. Some aid the immune response in the destruction of cancer or in the prevention of cancer spreading to other parts of the body.
The different types of Immunotherapy available are as follows :
Before understanding CAR T-cell immunotherapy, it is important for us to know what T-cells are.
Lymphocytes are white blood cells that aid in the fight against diseases, including cancer. They come in a variety of shapes and sizes, and T-cells are one such example of lymphocytes. These T-cells explore the body for infected cells and eliminate them.
When a person comes in contact with a new infection or virus, their body produces T-cells to help them fight it. It then stores some T-cells as a backup so that in case an infection recurs, the body will recognize it and tackle it right away.
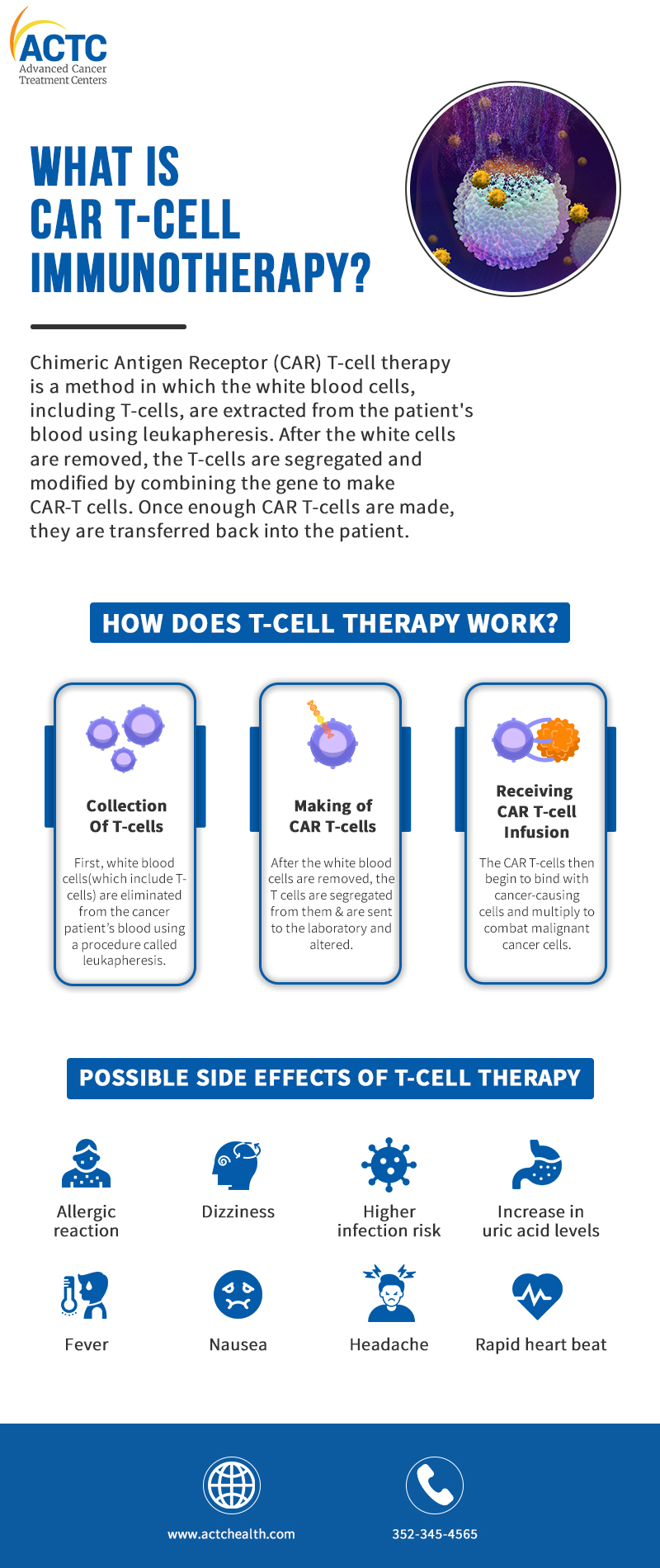
Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy is a method in which the white blood cells, including T-cells, are extracted from the patient's blood using leukapheresis. After the white cells are removed, the T-cells are segregated and modified by combining the gene to make CAR-T cells. Once enough CAR Ts are made, they are transferred back into the patient.
This therapy is sometimes called cell-based gene therapy because it involves altering the genes present inside the patient's T cells.
The treatment for CAR T-cell immunotherapy can take several weeks. It involves collecting T cells, sorting and transforming them and infusing them back into the patient.
.png)
First, white blood cells (which include T cells) are eliminated from the cancer patient's blood using a procedure called leukapheresis. During this procedure, patients usually lie down on a bed or sit on a recliner.
Two IV lines are needed in the collection process - as blood is to be removed from one line & put back into the body through another one after the separation of WBC's has taken place from it.
Sometimes during this process, blood calcium level drops which can cause numbness or muscle spasms. But this can be easily remedied by adding calcium to the blood, either by mouth or via the IV line.
After the white blood cells are removed, the T cells are segregated from them and are sent to the laboratory and altered by adding the gene for the specific chimeric antigen receptor (CAR). These are then grown and multiplied in the lab - which may take up to 6-8 weeks.
Once enough T-cells have been created, they will be administered to the patient. A few days before this immunotherapy, the patient may be given chemotherapy to help lower the number of other immune cells.
This gives CAR T-cells a better chance to activate and fight the cance- causing cells. The chemotherapy administered just before the infusion process is not very intense as these T-cells work best when they can find some cancer cells to attack. They begin to bind with cancer-causing cells and multiply to combat malignant cancer cells.
CAR T-cell therapy can be considered if conventional cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy are ineffective or if cancer recurs.
In the United States, the FDA has approved four CAR T-cell therapies. However, they can only be used to manage particular types of hematologic cancers in specific patient types, such as:
The National Library of Medicine in the United States, on the other hand, has approximately 600 current CAR T-cell treatment clinical trials. CAR T- cell immunotherapy is currently being researched for use in a variety of cancers, including:
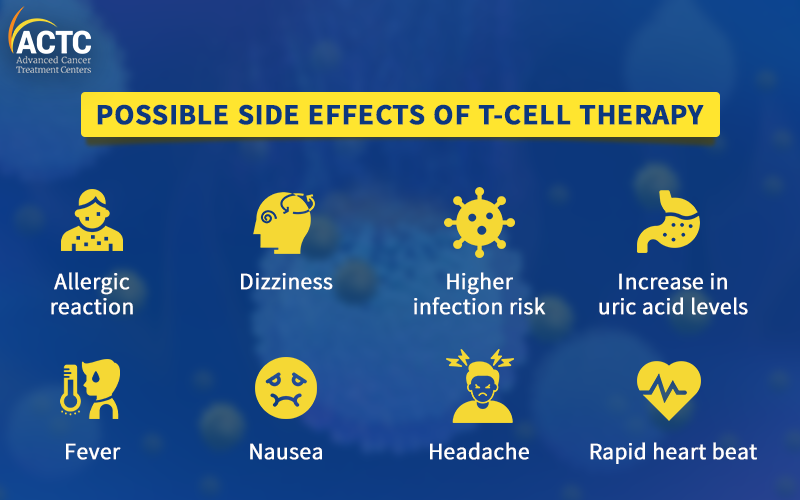
During the multiplication of CAR T-cells, a large amount of chemicals known as cytokines are released into the blood, which may disrupt the immune system and cause some side effects. Some of those are mentioned below:
The recovery period for patients who undergo CAR T-cell immunotherapy is about 2-3 months. Patients will be monitored for adverse effects and treatment response during this time frame. They are generally re-admitted to the hospital in order to deal with any problems.
Patients must stay near their treatment center for regular follow-up care for the first thirty days after receiving treatment. If required, a resource expert can aid with finding a place to stay during this period or they can choose a cancer treatment center which is located near their home.
As the patient's immune system improves, it may take some time for them to feel better. The CAR T-cell transfusion is usually followed by a 30-day healing period. Patients must stay at their care center or hospital during this period and must have a caregiver with them at all times to deal with the possibility of fever, infection, or other problems. During this time, patients can feel tired and have very little appetite.
CAR T-cell immunotherapy is a revolutionary treatment option for cancer that instructs the immune system to combat cancerous cells. T-cells are genetically modified to recognize and fight malignant cancer causing cells. Although the treatment is often beneficial, it does come with the potential of a few side effects for which providers are always ready.
CAR T-cell therapy is a relatively new treatment option limited to a few types of blood cancers. However, hundreds of more studies are currently being conducted to see if they can treat other cancers.
You can place your trust in the trained and experienced healthcare professionals at ACTC in Florida, and focus on healing and getting better. Our facility offers cutting-edge technology to provide each cancer patient with the most personalised therapy and care possible for best possible outcomes.
Infographic:


January 07, 2026
A chemo port is a small device placed under your skin that makes recei...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
It's natural to wonder if testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is sa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A rash that will not calm down is scary, especially when it changes or...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Florida’s lung cancer burden remains significant and affects many fa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A partial hysterectomy, also called a supracervical hysterectomy, is s...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Finding a rash on your breast can be unsettling, but remember, many ra...
KNOW MORE
