
Book a Consultation
Thank you!
Your form has been sent successfully.


March 25, 2021
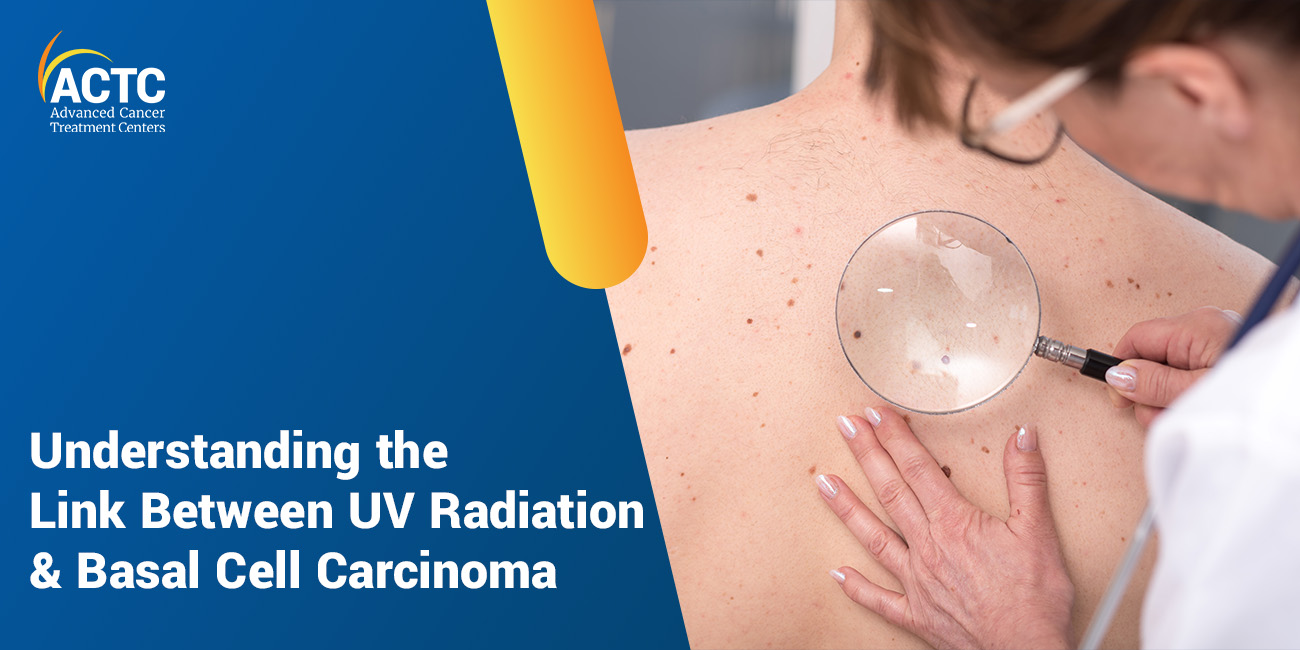
Ultraviolet radiation (UV) refers to a short wavelength electromagnetic band spectrum that is invisible to the human eye. Sources of UV radiation found in everyday life include the sun, tanning beds, and black lights. While we may not be able to see it, certain types of UV radiation may pose a serious health risk and lead to basal cell carcinoma and other types of skin cancer.
Skin cancers are abnormal growths that start in the cells that comprise the epidermal layers of the skin. Basal cell carcinoma (BCC), squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), and melanoma are common skin cancer subtypes affecting different cells of the skin. BCC is the most common type, affecting the inner layer of the epidermis where new skin cells are made. SCC affects the middle and outer layer of the epidermis. Malignant melanoma originates in the pigment-producing cells of the inner layer of the epidermis.
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) functions as a chemical storage medium for genetic information. DNA is contained within packages called chromosomes (highly compacted strands of DNA) that exist within the nuclei of every living cell in the human body and determines everything about you from the color of your hair to how tall you are to how long you will live.
The structure of DNA is composed of a phosphate group bound to a sugar (ribose) which forms the helix “backbone” of the molecule. The phosphate-sugar backbone is bound to a base - either cytosine, guanine, adenine or thymine - forming a nucleotide. Complementary nucleotides bond to one another to form a tight double-helix coil.
Frequent and ample exposure to harmful UV radiation has been shown to cause significant increases in risk of the development of skin cancer in humans via direct damage to DNA.
Although most of the UV spectrum is absorbed efficiently by atmospheric gases rendering the radiation ineffective, ultraviolet A (UVA) and ultraviolet B radiation (UVB) pass through and are readily absorbed by cellular life on earth.
The pigment melanin provides our skin with some protection against the sun, but some UV radiation is inevitably absorbed. Most of the radiation absorbed is transformed into heat, but the small amount that may change the chemical structure of the DNA molecules in unpredictable ways resulting in lesions at sites along the DNA strand.
Read more: A Gift Guide for Cancer Fighters
DNA lesions are classified based on their features:
In skin cancer, mismatch lesions presenting as covalent bonds among two thymine nucleobases are the direct result of overexposure to UVB. The damage caused may eventually lead to mutations that interrupt normal DNA repair processes, causing abnormal growth. In more than 50% of BCC cases, there is evidence of a mutation in tumor suppressor gene p53, rendering it inactive.
Read more: Making the Best of Life After Cancer

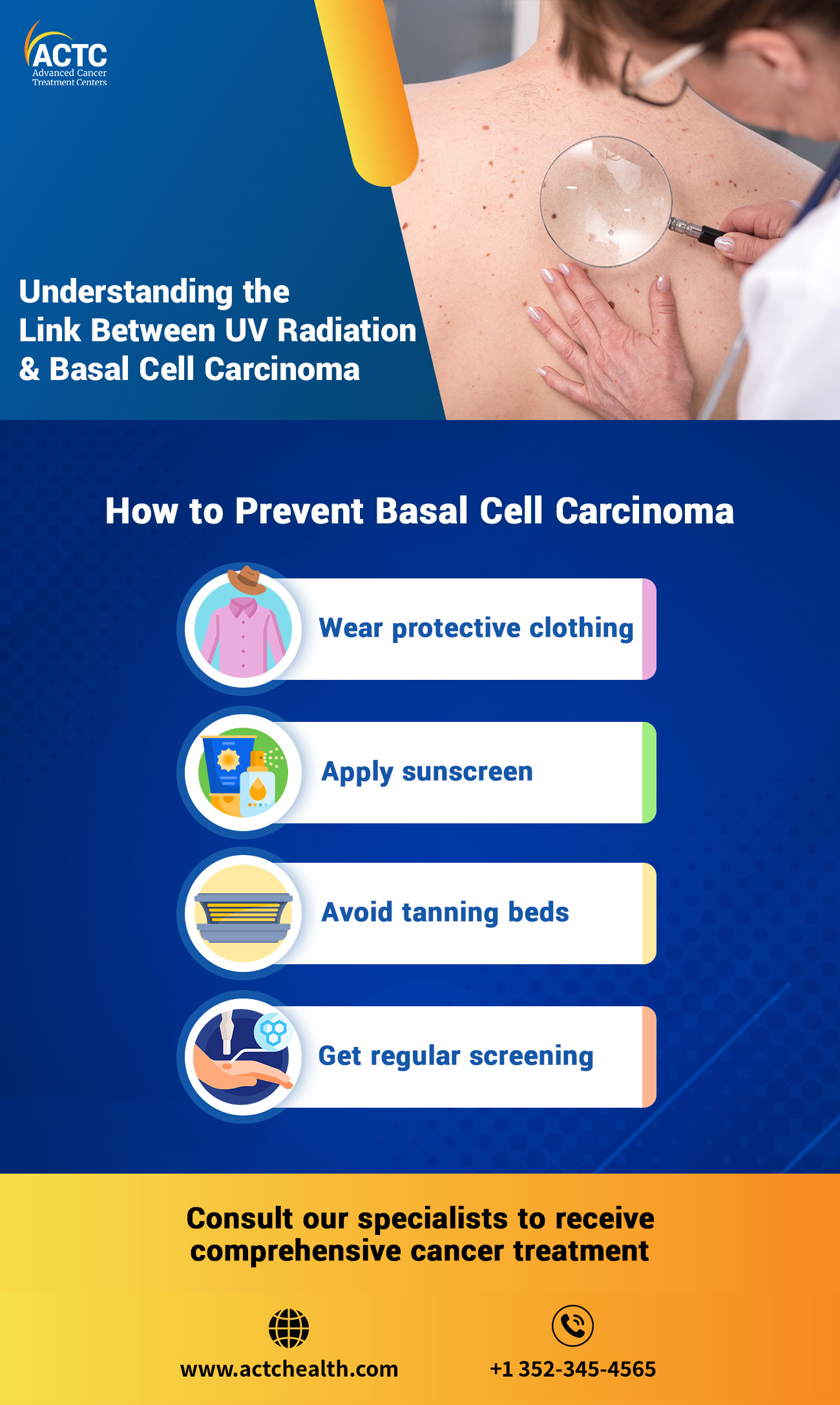
Protecting yourself from the sun is the first step in reducing your risk of developing skin cancer. The following are a few steps one may take to minimize radiation exposure and prevent basal cell carcinoma and other types of skin cancer.
Use protective clothing that covers as much skin as possible. Wear long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses with UV protection to shield the face, neck, and eyes from direct sunlight.
Additionally, avoid outdoor activities during peak UV radiation hours, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. Try to find shelter under trees, umbrellas, or use sun-protective structures when spending time outdoors.
Do not forget to apply an ample amount of sunscreen when stepping out. Selecting a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high sun protection factor (SPF) is crucial to minimize the effects of UV radiation on the skin. Reapply the sunscreen every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating for more effective results.
Artificial UV radiation sources like tanning beds can significantly increase the risk of skin cancer. Individuals may opt for safer alternatives like self-tanning products for a tan appearance.
Self-examinations and regular visits to dermatologists for skin cancer screenings can go a long way to help individuals minimize their risk. Early detection plays a critical role in successful treatment.
According to researchers, skin cancer is the most commonly diagnosed type of cancer in the United States. As the number of skin cancer cases rises every year, early detection becomes more crucial to reduce the risk of mortality. Consult the experts at Advanced Cancer Treatment Centers if you have any concerns about the risk factors for skin cancer.
If you have any questions or concerns, call (352) 597-4998 or follow this link to request an appointment online.


January 07, 2026
A chemo port is a small device placed under your skin that makes recei...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
It's natural to wonder if testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is sa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A rash that will not calm down is scary, especially when it changes or...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Florida’s lung cancer burden remains significant and affects many fa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A partial hysterectomy, also called a supracervical hysterectomy, is s...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Finding a rash on your breast can be unsettling, but remember, many ra...
KNOW MORE
