
Book a Consultation
Thank you!
Your form has been sent successfully.



March 25, 2021
The most commonly diagnosed form of blood cancer in the United States is Lymphoma. This is a type of cancer that affects lymphocytes, commonly known as white blood cells. Lymphocytes are important in the body's defense against external invaders such as bacteria and viruses.
Those who have autoimmune diseases or those who take immuno-suppressants are at significantly higher risk for lymphoma. Although it is a type of blood cancer, lymphoma can affect any organ in the body.
Lymphoma is a form of malignancy that starts in the immune system's infection-fighting cells called lymphocytes. The lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, bone marrow, and other areas of the body contain these cells. The lymphocytes in lymphoma mutate and expand in a rapid and uncontrolled fashion.
There are two types of lymphoma: Non-Hodgkin lymphoma and Hodgkin lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is the most common kind of lymphoma. Different types of lymphocyte cells are involved in non-Hodgkin and Hodgkin lymphoma. Each form of lymphoma develops at a distinct rate and responds to treatment in a different way.
Reed-Sternberg cells are present in Hodgkin lymphoma, which distinguishes it from other lymphoma types. These are big, malignant cells seen in Hodgkin lymphoma tissues, and they're named after the researchers who discovered them. Hodgkin lymphoma cancer is one of the most easily treatable cancers.
In the large majority of cases, scientists have no idea what causes lymphoma.
People at greater risk include those who are:
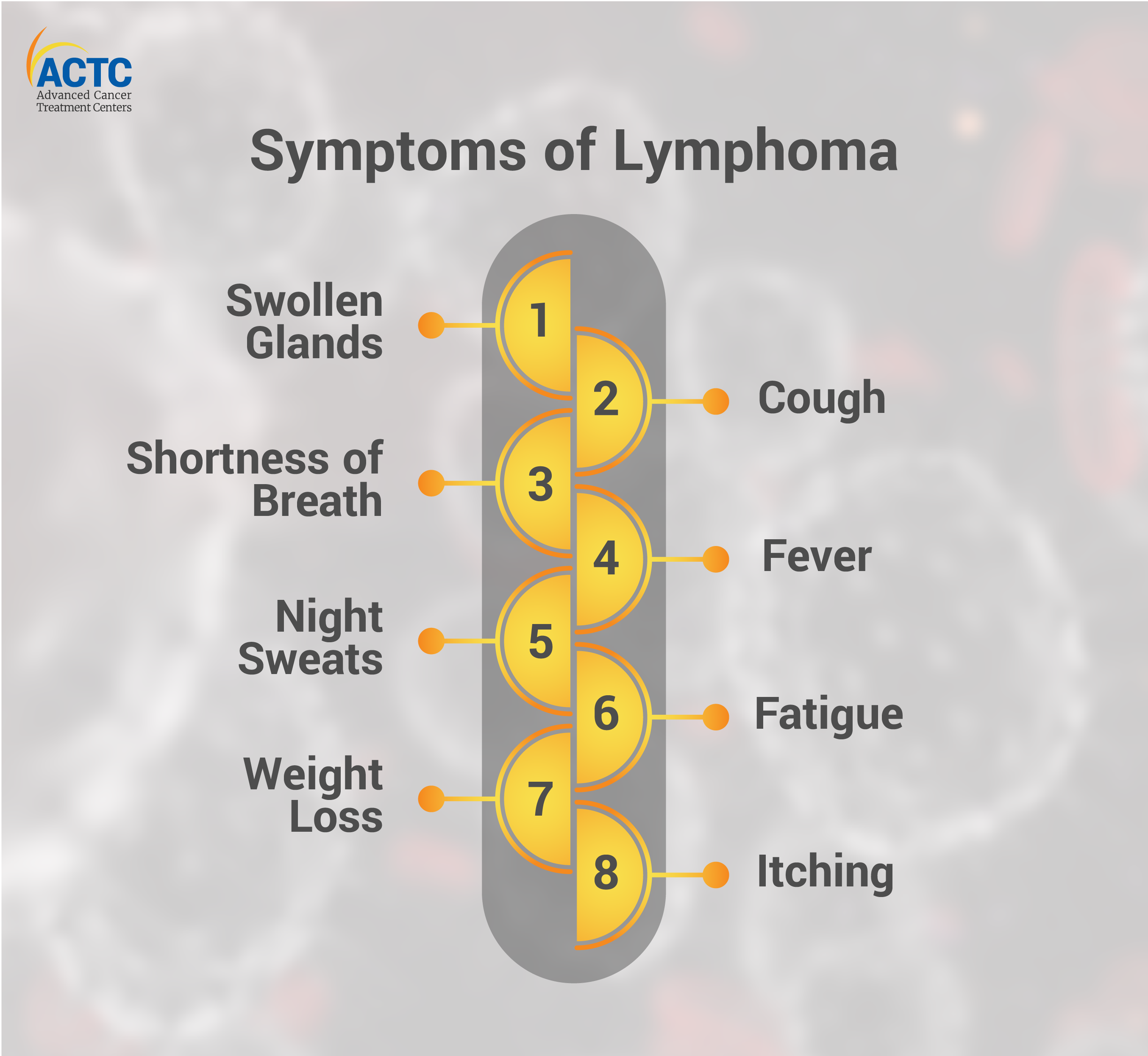
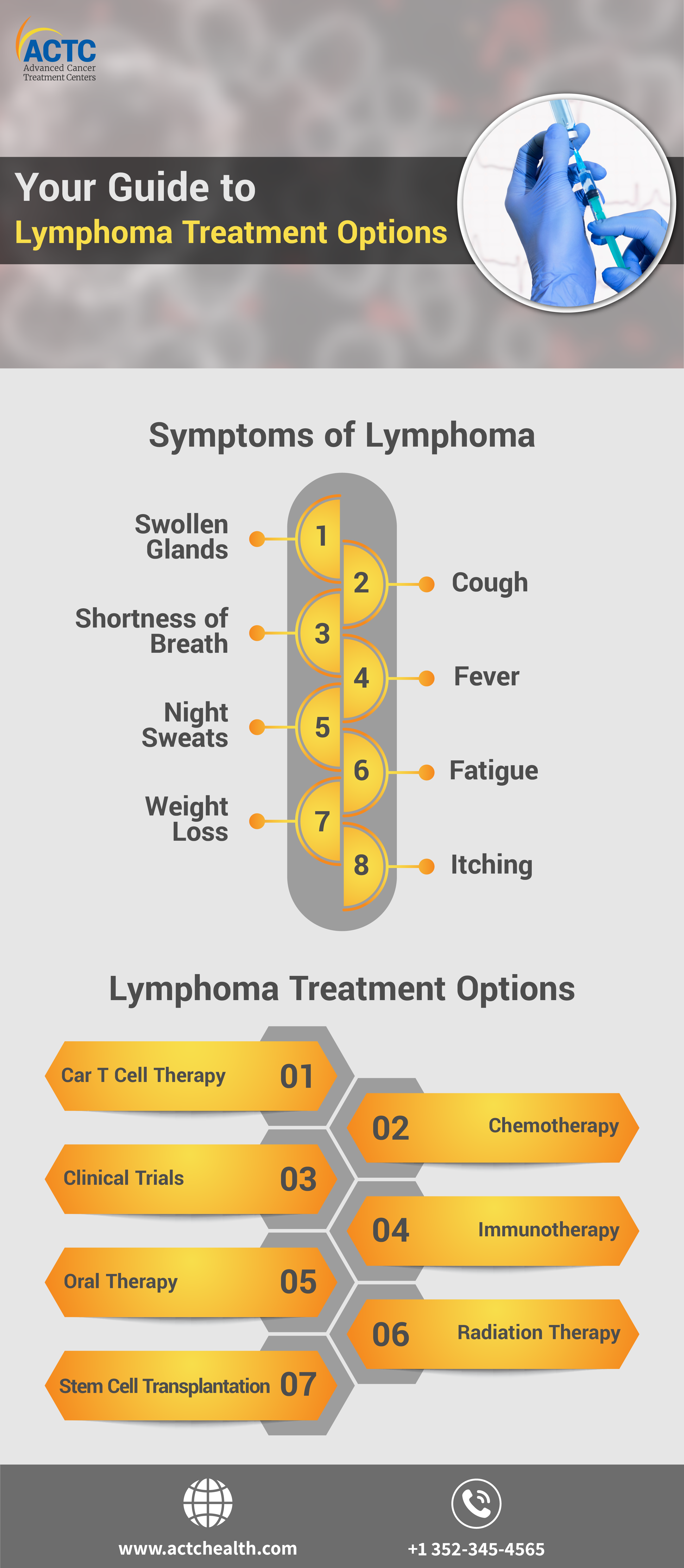
Lymphoma has several warning indicators, including:
Many of these signs and symptoms can also indicate the presence of other disorders. Consult your doctor who will prescribe the diagnostic tests you require.
Your doctor will do a physical examination, which will include a look for swollen lymph nodes. This symptom may not necessarily indicate that you have cancer. Swollen lymph nodes are usually caused by an infection that is unrelated to cancer.
A lymph node biopsy may be performed to look for cancer cells. A doctor will remove all or part of a lymph node for this test, or withdraw a little bit of tissue from the afflicted node with a needle.

The treatment options for lymphoma vary considerably and are often combined. Your lymphoma treatment plan will be determined by criteria such as your age, overall health, lymphoma type, tumor size, and location.
Treatments for lymphoma include:
Engineered molecules known as chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) are used in CAR T Cell Therapy to recognize and eliminate antigens on the surface of lymphoma cells.
Engineered molecules known as chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) are used in CAR T Cell Therapy to recognize and eliminate antigens on the surface of lymphoma cells.
Chemotherapy is used to kill cancerous cells. It's primarily used to treat cancer that has spread throughout the body, which is known as systemic cancer. Instead of single-agent therapy, many lymphoma patients receive a combination of chemotherapy, which consists of two or more medicines.
Patients at all stages of the disease can benefit from clinical trials. A clinical trial's goal is to safely track a drug's effects on patients over time in order to find more effective treatments for certain conditions. Clinical trials allow patients to receive quality care in a highly controlled and supportive environment.
Immunotherapy (also known as immune-oncology) is a word that refers to treatments that work with the immune system. The immune system's job is to rid the body of dangerous pathogens including bacteria and viruses, as well as cancer cells.
Many oral anticancer medicines are licensed for the treatment of lymphoma and are available in liquid, tablet, or capsule form. Oral anticancer medications are just as effective as intravenous anticancer treatments.
High-energy x-rays are used in radiation therapy (also known as radiotherapy) to destroy cancer cells and shrink tumors. Radiation is a local therapy, meaning it only affects cancer cells in the area being treated. Radiation is sometimes used alone or in combination with chemotherapy for some localized lymphomas, whether nodal or extranodal.
Because stem cells can be transplanted, doctors can use larger doses of chemotherapy to treat cancer than the body can ordinarily handle, increasing the likelihood of cancer cells being destroyed. In the case of chemotherapy followed by stem cell infusion, new stem cells can replace cells that were affected by the chemotherapy treatment.
If you are looking for an advanced cancer care center in Florida for a loved one suffering from lymphoma, we can help. At ACTC, we offer evidence-based cancer treatment that is personalized for each individual. We have some of the most experienced Florida cancer doctors on our team. To schedule an appointment, please call 352-345-4565.


January 07, 2026
A chemo port is a small device placed under your skin that makes recei...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
It's natural to wonder if testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is sa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A rash that will not calm down is scary, especially when it changes or...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Florida’s lung cancer burden remains significant and affects many fa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A partial hysterectomy, also called a supracervical hysterectomy, is s...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Finding a rash on your breast can be unsettling, but remember, many ra...
KNOW MORE
