
Book a Consultation
Thank you!
Your form has been sent successfully.



September 22, 2025
Medical imaging tests are key tools in cancer care. They help your doctor find cancer, determine how far it has spread (stage), and monitor how well your treatment is working.
Each type of imaging test provides different information: CT scans show detailed pictures of structures in your body, while PET scans show how your body’s tissues are functioning.
Often, doctors combine both tests (PET and CT) to get a complete view. Let’s start by looking closely at CT scans.
A CT (computed tomography) scan uses medical X-rays to take slice-like images of your internal organs. During the scan, you lie comfortably on a table that moves slowly through a doughnut-shaped scanner.
The scanner takes multiple X-ray pictures from different angles. A computer then puts these slices together into clear, detailed, three-dimensional pictures of your organs. Doctors use CT scans to identify tumors or other abnormalities quickly and accurately.
Clear detail: CT scans capture high-quality images, clearly showing even small abnormalities or tumors.
Fast and painless: A typical CT scan takes just minutes, is noninvasive, and causes no discomfort.
Versatile imaging: CT can clearly image your chest, abdomen, pelvis, and bones.
Easy access: CT scans are widely available in most hospitals and imaging centers.
Radiation exposure: CT uses small amounts of radiation. One scan carries low risk, but multiple scans over time add up.
Contrast dye risks: Some scans require contrast dye, a medicine used to highlight organs. Rarely, people have allergic reactions or kidney problems from this dye.
False alarms: Sometimes, CT scans show harmless spots that may require additional tests to rule out cancer.
A PET (positron emission tomography) scan is another type of imaging test that uses a tiny amount of radioactive sugar (tracer). The tracer is injected into the bloodstream and absorbed by cells throughout the body.
Cancer cells often absorb more sugar, which is clearly visible during the scan. A special camera detects signals from the tracer to produce detailed three-dimensional pictures showing tissue activity. This gives your doctor valuable information about how your organs and tissues are functioning.
Highly sensitive: PET scans are very good at detecting active disease, even small tumors or abnormalities that other tests might miss.
Shows organ function: PET clearly shows how tissues and organs are working, helping doctors spot cancer earlier.
Treatment guidance: PET scans can show if chemotherapy or radiation therapy is effective.
Radiation exposure: PET uses a small amount of radiation that fades quickly after the test.
Tracer leaves quickly: Most of the radioactive tracer leaves your body naturally within a day or two through bodily fluids.
Limited availability: PET scans aren’t as widely available as CT scans and may require travel to specialized centers.
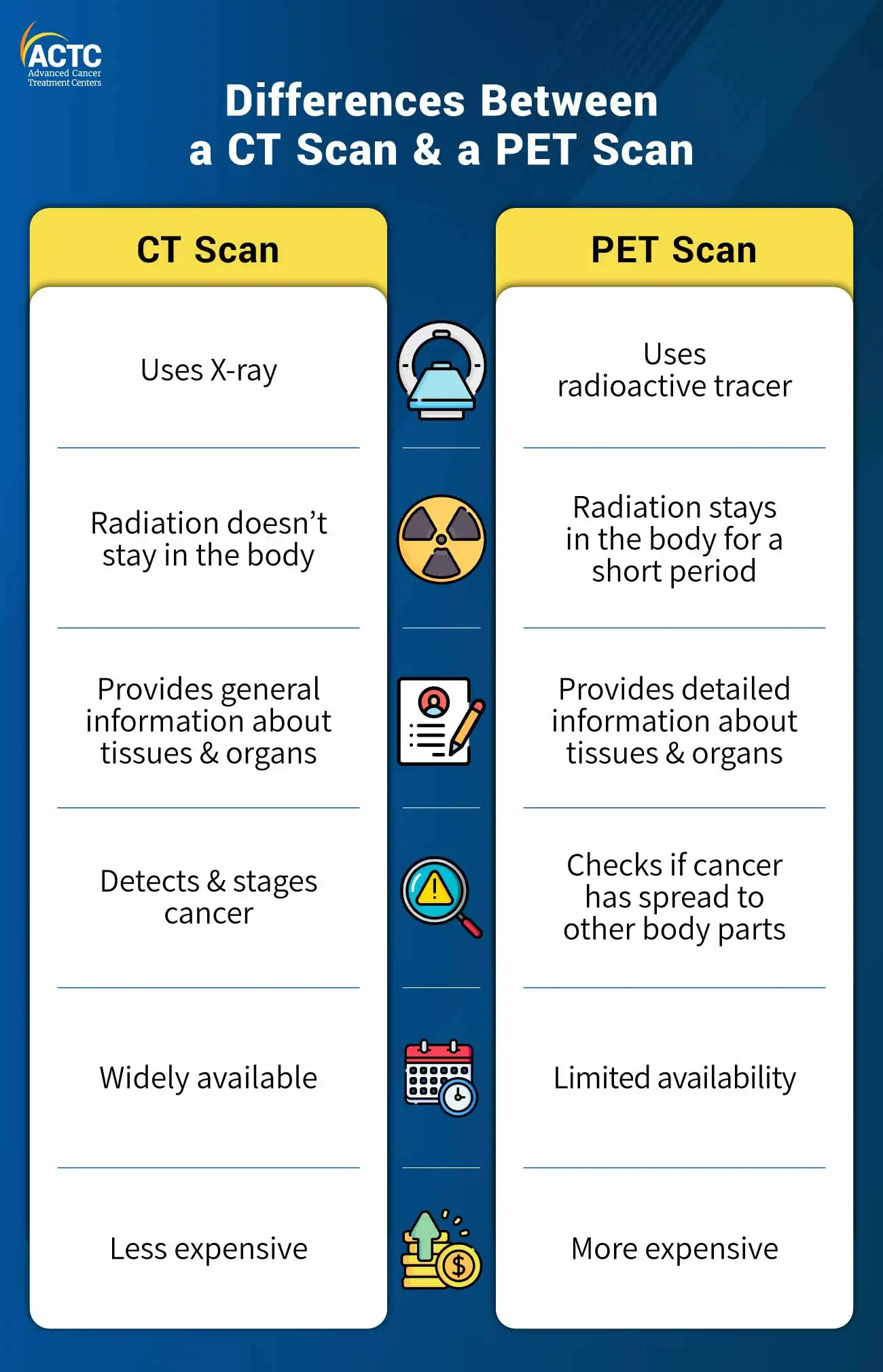
Below is a table comparing the differences between a CT and a PET scan:
| Feature | CT Scan | PET Scan |
| Radiation source | Medical X-rays | Radioactive tracer (sugar-based) |
| Images provided | Detailed structural (anatomical) images | Shows how tissues function |
| Radiation afterward | None remains in body after scan | Small amount briefly remains |
| Role in cancer care | Detecting, staging tumors | Checking spread, treatment results |
| Availability & cost | Widely available, typically lower cost | Less available, higher cost |
Combining PET and CT scans into a single PET-CT procedure can enhance diagnostic accuracy by pairing structural detail (CT) with tissue activity (PET).
Doctors often order PET-CT to check how effectively cancer treatments are working. Your care team chooses the right imaging based on your individual needs and specific cancer diagnosis.
The best imaging test for you depends on the type of cancer you have and what your doctor needs to know at this stage in your care. Your imaging plan will balance benefits, safety, and the clarity of information required.
To learn more about cancer treatment options, contact ACTC, one of the best cancer treatment centers in Florida, and schedule an appointment. Call 352-345-4565 or book an appointment.


January 07, 2026
A chemo port is a small device placed under your skin that makes recei...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
It's natural to wonder if testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is sa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A rash that will not calm down is scary, especially when it changes or...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Florida’s lung cancer burden remains significant and affects many fa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A partial hysterectomy, also called a supracervical hysterectomy, is s...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Finding a rash on your breast can be unsettling, but remember, many ra...
KNOW MORE
