
Book a Consultation
Thank you!
Your form has been sent successfully.



February 27, 2023
Testicular cancer is a rare type of cancer that affects the testicles- the male reproductive glands located in the scrotum. The testicles produce and store sperm, as well as the male hormone testosterone. Testicular cancer is one of the most curable cancers, especially when detected early.

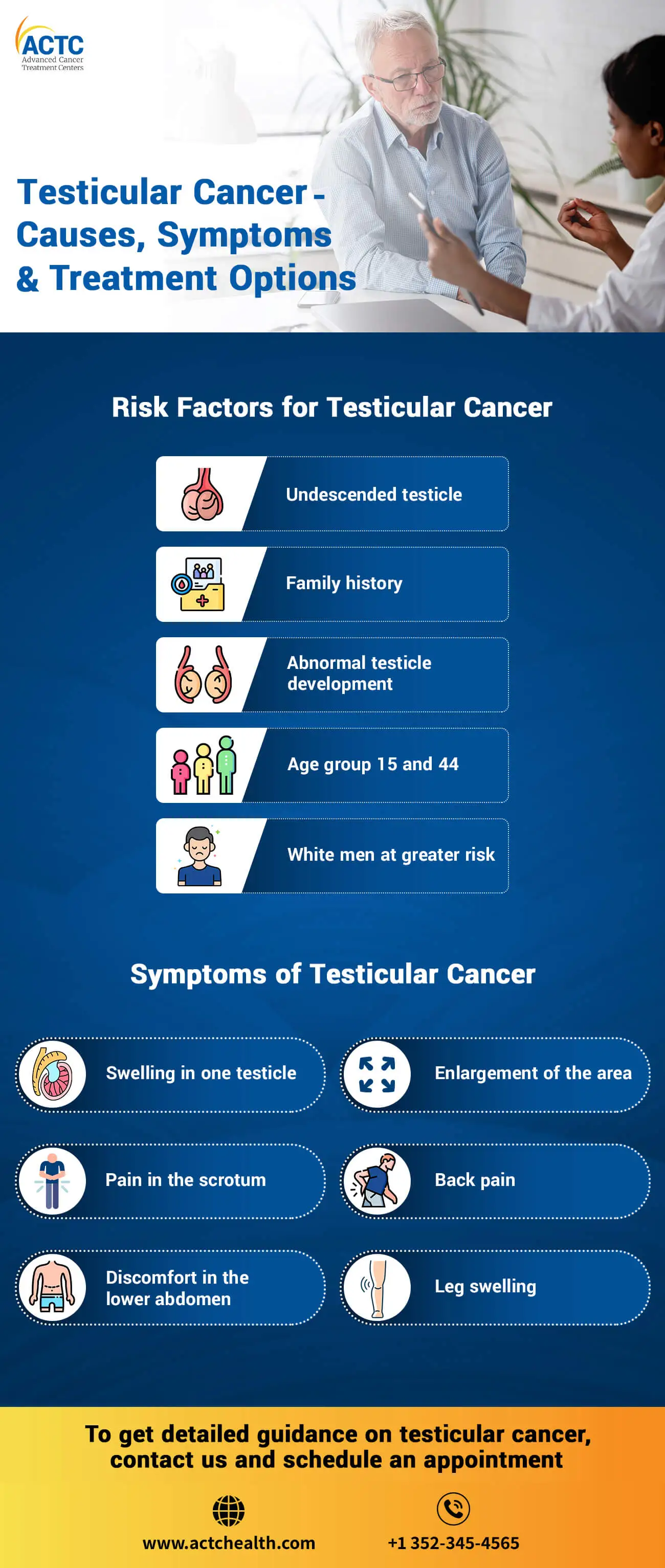
Although the exact cause of testicular cancer is unknown, several risk factors may increase the likelihood of developing the disease. The risk factors are as follows:
Undescended testicle or cryptorchidism- When a testicle does not descend into the scrotum before birth, it is known as an undescended testicle, or cryptorchidism. Men with undescended testicles are at a higher risk for this disease.
Family history of testicular cancer- If a man has a close relative, such as a father or brother, who has been diagnosed with testicular cancer, he may be at an increased risk.
Abnormal testicle development- Men suffering from any condition that affects testicular development, such as Klinefelter syndrome, can develop this disease.
Age- It is most commonly diagnosed in young men between the ages of 15 and 44 and the risk decreases with age.
Race- White men are at greater risk than any other race.
It is important to note that having one or more of these risk factors does not mean that a man will develop testicular cancer.

The symptoms can vary for every individual depending on the stage of cancer. But the common signs may include:
If someone experiences any of these symptoms, it is crucial to see a doctor as soon as possible for a proper diagnosis.
Testicular cancer is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, imaging tests, and biopsy. Ultrasound is the most common noninvasive procedure that helps determine if a lump in the testicle is a solid mass (may indicate cancer) or a fluid-filled cyst (usually not cancerous). On the other hand, doctors recommend blood tests to check if the body is producing higher-than-normal levels of some proteins, such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) or human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), which may indicate this disease.
Treatment for any type of cancer typically depends on the type and stage, as well as the health condition of an individual. Some of the most common testicular cancer treatment options include:
Surgery- The most common treatment for testicular cancer is surgery to remove the affected testicle, also known as orchiectomy. In most cases, the unaffected testicle can compensate for the affected testicle.
Radiation therapy- Doctors may recommend a combination of radiation therapy and surgery to prevent testicular cancer from spreading to other organs.
Chemotherapy- It is typically used to treat more advanced cases of testicular cancer, or if cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
In some cases, particularly if the cancer is in an early stage and has not spread to any other organs beyond the testicles, a doctor may recommend observation instead of immediate treatment. Instead, they monitor the patient closely, without immediately starting treatment, to see if it grows or spreads. Discuss all possible treatment plans with a doctor to make a well-informed decision.
Although there is currently no sure way to prevent testicular cancer, some lifestyle changes and precautions can reduce the risk. Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding harmful substances such as tobacco and excessive alcohol, may help reduce the risk. Also, seek immediate medical attention for any testicular conditions, such as testicular torsion or inflammation like epididymitis.
A self-examination is an important tool in detecting testicular cancer early, as it allows an individual to check for any changes or lumps in the testicles. Early detection is crucial in improving the chances of successful treatment, as testicular cancer can be highly treatable when caught in its early stages. It is best to perform a self-exam after a warm bath or shower, as the heat may cause the scrotum to relax, making it easier to detect any changes.
If any changes or lumps are visible during a self-exam, or any there’s any persistent pain or discomfort in the area, schedule a doctor's appointment as soon as possible. Contact ACTC, one of the best cancer treatment centers in Florida and schedule an appointment with our providers.


January 07, 2026
A chemo port is a small device placed under your skin that makes recei...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
It's natural to wonder if testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is sa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A rash that will not calm down is scary, especially when it changes or...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Florida’s lung cancer burden remains significant and affects many fa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A partial hysterectomy, also called a supracervical hysterectomy, is s...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Finding a rash on your breast can be unsettling, but remember, many ra...
KNOW MORE
