
Book a Consultation
Thank you!
Your form has been sent successfully.



July 14, 2023
The adrenal glands are a pair of small, triangular-shaped endocrine glands located on top of each kidney, regulating numerous physiological processes and bodily functions. Tumors in the adrenal glands may form due to various factors, including genetic mutations, hormonal imbalance, and abnormalities during fetal development. The most common types of tumors are adrenal adenomas, which are usually benign (non-cancerous). Malignant (cancerous) adrenal gland tumors, also known as adrenocortical carcinomas, are relatively rare
Diagnosing adrenal gland tumors is comparatively difficult since the symptoms can be diverse and non-specific, often overlapping with other conditions. However, advancements in medical imaging techniques and laboratory tests have significantly improved the accuracy of diagnosis, enabling healthcare professionals to identify these tumors with greater precision.
In this blog post, we will share detailed insights into adrenal gland tumor diagnosis, staging, and treatment options. Read on to learn more.

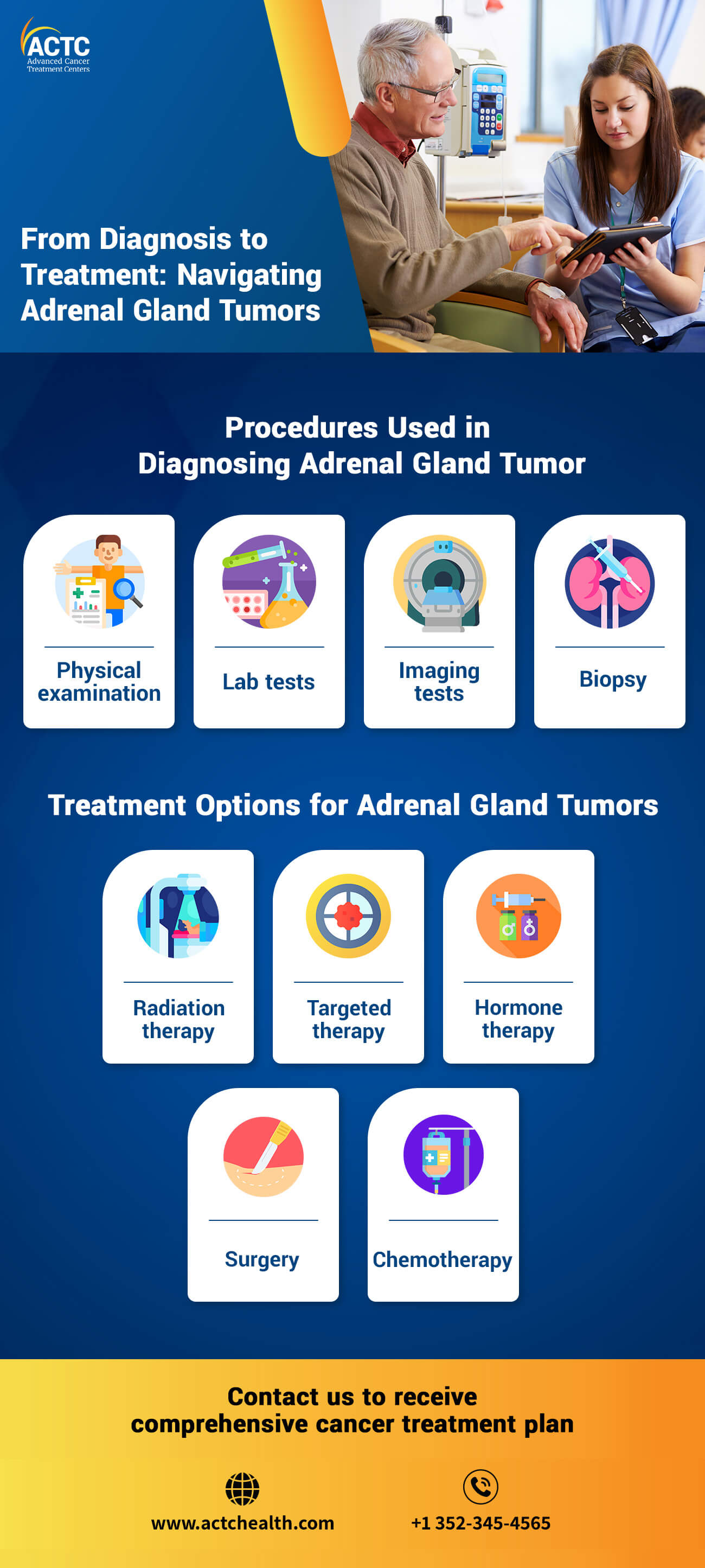
Those exhibiting symptoms of adrenal gland tumors need to consult a physician for a confirmed diagnosis. The following are some of the common diagnostic procedures for this condition:
A healthcare provider will analyze the medical history, including symptoms and family history of an individual. They will then conduct a thorough physical examination to assess any signs or abnormalities that may indicate the presence of adrenal gland tumors.
Oncologists usually perform this test to confirm a cancer diagnosis. In a biopsy, providers obtain a tissue sample from the tumor through a minimally invasive procedure guided by imaging techniques. Then they examine the sample under a microscope to determine the tumor's characteristics and whether it is benign or malignant.
After a confirmed diagnosis, healthcare providers determine the stages to guide treatment decisions and provide valuable prognostic information.
Healthcare providers use the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM system, which stands for Tumor, Node, and Metastasis, to determine the stage of the tumors. Here is an overview of how oncologists use the TNM system to stage adrenal gland tumors:
T denotes the size of the primary tumor and its invasion into neighboring areas.
N signifies the spread of regional lymph nodes surrounding the adrenal gland. Lymph nodes are small clusters of immune system cells where the cancers metastasize initially.
M indicates whether cancer has been disseminated (metastasized) to distant locations, such as other organs or lymph nodes that are not located near the adrenal gland.
T1, N0, M0
This stage is further divided into three sub-stages, which are as follows:
This stage is further divided into two sub-stages, which are as follows:
Any T, Any N, M1

It is the primary treatment for adrenal gland tumors that involves the removal of the tumor and, in some cases, the entire adrenal gland. Oncologists typically recommend surgery for localized tumors, including stage I and II, and some stage III tumors.
This traditional cancer treatment procedure uses high-energy X-rays or other forms of radiation to destroy cancer cells. Radiation therapy is often used as the primary treatment for inoperable or metastatic adrenal gland tumors or as adjuvant therapy after surgery. It can cause mild to severe side effects such as fatigue, skin changes, etc.
This cancer treatment option involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. Oncologists typically use it to treat advanced adrenal gland tumors that have spread extensively (stage IV) or are unresponsive to other treatments. Chemotherapy may produce side effects such as hair loss, nausea, and increased risk of infections.
It is a cancer treatment option where oncologists use certain drugs to specifically target genetic or molecular abnormalities present in tumor cells. The drugs used in targeted therapy aim to block specific pathways that escalate tumor growth and progression. Targeted therapy may be used in cases where tumors have specific genetic mutations or when other treatments have been ineffective.
It involves the use of medications to control the production and effects of hormones in cases where the tumor is hormone-producing. It aims to reduce hormone levels and manage related symptoms. Hormone therapy may be used alongside other treatments or as a palliative approach for advanced cases.
The choice of treatment and its effectiveness depends on factors such as the type of tumor, stage, and overall health of individuals.
After receiving treatment for adrenal gland tumors, follow-up care is crucial to monitor the patient's recovery, detect potential recurrence or complications, and provide ongoing support. Individuals should attend scheduled follow-up appointments with their cancer care team to minimize the risk of recurrence or treatment-related complications.
For any queries or concerns about adrenal gland tumors, contact ACTC, one of the best cancer treatment clinics in Florida, offering comprehensive, personalized cancer treatment plans. Our cancer treatment center has state-of-the-art facilities to provide the best possible cancer care.


January 07, 2026
A chemo port is a small device placed under your skin that makes recei...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
It's natural to wonder if testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is sa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A rash that will not calm down is scary, especially when it changes or...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Florida’s lung cancer burden remains significant and affects many fa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A partial hysterectomy, also called a supracervical hysterectomy, is s...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Finding a rash on your breast can be unsettling, but remember, many ra...
KNOW MORE
