
Book a Consultation
Thank you!
Your form has been sent successfully.



January 27, 2023
Bladder cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the bladder, a balloon-shaped organ in the pelvis that stores urine. It is the sixth most common type of cancer in the United States and is more common in men than women. Most bladder cancers begin in the urothelium, the innermost layer of the bladder, which is made up of cells that line the inside of the bladder.
According to the American Cancer Society*, bladder cancer accounts for about 5% of all new cancer cases in the United States. In 2022, an estimated 81,180 people were diagnosed with this cancer.
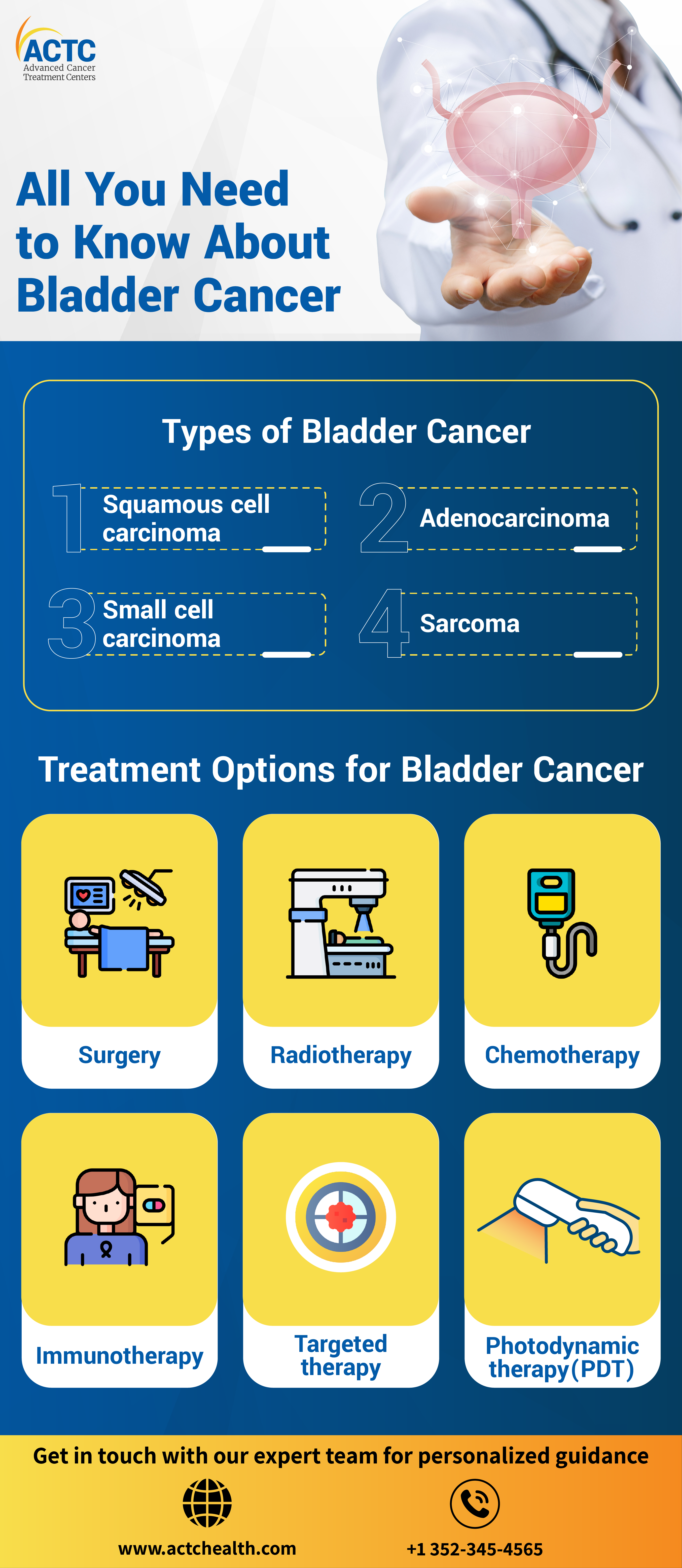
Squamous cell carcinoma - It is linked to persistent bladder irritation, either brought on by an infection or from using a urinary catheter for an extended period.
Adenocarcinoma - It is a rare kind of cancer that can develop primarily in the bladder or other organs as a secondary cause.
Small cell carcinoma - It is an uncommon and deadly variety that displays biological traits comparable to those associated with small-cell lung cancer.
Sarcoma - Bladder sarcomas frequently start in the bladder's fat or muscular layers. This is a rare kind with a high likelihood of cancer spreading to other areas of the body.
Read More: A Gift Guide for Cancer Fighters
Understanding the risk factors associated with bladder cancer can help to decrease the risk of developing this disease. While these risk factors increase the risk of bladder cancer, they do not necessarily mean that every person who has these risk factors will develop cancer.
1. Smoking - Cigarettes or other tobacco products are the greatest risk factor for bladder cancer.
2. Age - Bladder cancer is more common in people aged 60 and above.
3. Gender - Men are three to four times more likely to develop bladder cancer than women.
4. Race - White people are more likely to develop this cancer than African Americans.
5. Exposure to certain chemicals - Certain chemicals, such as those used in manufacturing rubber, leather, and dye industries, have been linked to an increased risk of this disease.
6. Personal history of bladder cancer - A previous diagnosis of bladder cancer increases the risk of a recurrence.
7. Family history - It can be hereditary and having a family member with bladder cancer increases the risk.
8. Chronic bladder inflammation - People with long-term bladder infections or other chronic bladder problems are at a higher risk.
9. Diabetes - People with diabetes are more likely to develop this cancer.
Read More: 8 lifestyle changes that could reduce your cancer risk
Some of the common symptoms of bladder cancer are as follows:
Blood in the urine (hematuria): The most common symptom of this disease is red or pink-colored urine. According to the American Cancer Society, about half of people with bladder cancer will develop hematuria.
Changes in urination: Painful or burning sensation during urination, urinating more often than usual, feeling the need to urinate urgently, feeling the need to urinate, but nothing happens, etc. could be possible symptoms of bladder cancer.
The individual with advanced bladder cancer might also experience the following symptoms
Seek medical attention immediately in case any of these symptoms are visible. Early detection of can help improve treatment outcomes and increase the chances of good pronosis.

The treatment options for bladder cancer depend on the type, size, stage, and the overall health of the patient. The top five common forms of treatment are as follows:
1. Surgery - This may involve removing part or all of the bladder, as well as nearby lymph nodes and other organs.
2. Radiotherapy - High-energy radiation may be used to kill cancer cells. It is used as a primary treatment to destroy cancer cells or as an adjuvant therapy.
3. Chemotherapy - It works by killing rapidly-dividing cancer cells and inhibiting the growth of new ones. It is usually administered as a combination of drugs that are taken orally or intravenously.
4. Immunotherapy - This uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. It can help reduce the size of the tumor, relieve symptoms, and improve the overall outcome of treatment.
5. Targeted therapy - Targeted therapy uses drugs or other substances to target and attack specific cancer cells. It helps to slow or even stop the progression of the disease.
6. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) - In PDT, cancer cells are killed by a special type of light and a light-sensitive drug. PDT can be used to destroy bladder tumors that are too large or too deep to be removed with surgery.
Bladder cancer is a serious, life-threatening condition affecting thousands of people every year. It is important to be aware of the risk factors, symptoms, and treatments for this disease so that it can be diagnosed and treated promptly. Therefore, be cautious and do not skip routine screenings and examinations. To receive the best cancer care, contact Advanced Treatment Centers in Florida and consult with our board-certified oncologists.
*Data provided by American Cancer Society


January 07, 2026
A chemo port is a small device placed under your skin that makes recei...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
It's natural to wonder if testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is sa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A rash that will not calm down is scary, especially when it changes or...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Florida’s lung cancer burden remains significant and affects many fa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A partial hysterectomy, also called a supracervical hysterectomy, is s...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Finding a rash on your breast can be unsettling, but remember, many ra...
KNOW MORE
