
Book a Consultation
Thank you!
Your form has been sent successfully.



May 04, 2023
The vagina is a canal that extends from a woman's uterus to the outside of her body. Vaginal cancer happens when the vaginal cells grow abnormally and rapidly. This is a rare form of cancer, with approximately 6,000 new cases being diagnosed in the U.S every year.
In this blog post, we will understand vaginal cancer symptoms, causes, how it is diagnosed, and what the treatment options are. Read on to learn more.

It is the most common form of vaginal cancer that occurs when cancer forms in the flat, thin cells, lining the vaginal wall. This cancer is localized and grows slowly. However, if detected at an advanced stage, squamous cell carcinoma can spread to distant organs like the liver, lungs, or bones.
This type of vaginal cancer starts in the glandular cells in the lining of the vagina, responsible for making mucus and other fluids. Adenocarcinoma can spread rapidly and quickly to other areas, including the lungs and the lymph nodes in the groin.
This is the rarest type that often affects women whose mothers took diethylstilbestrol (DES) in the early months of pregnancy. It was a common medication that doctors used to prescribe between 1938 and 1971 to prevent miscarriages and other difficulties during pregnancy.
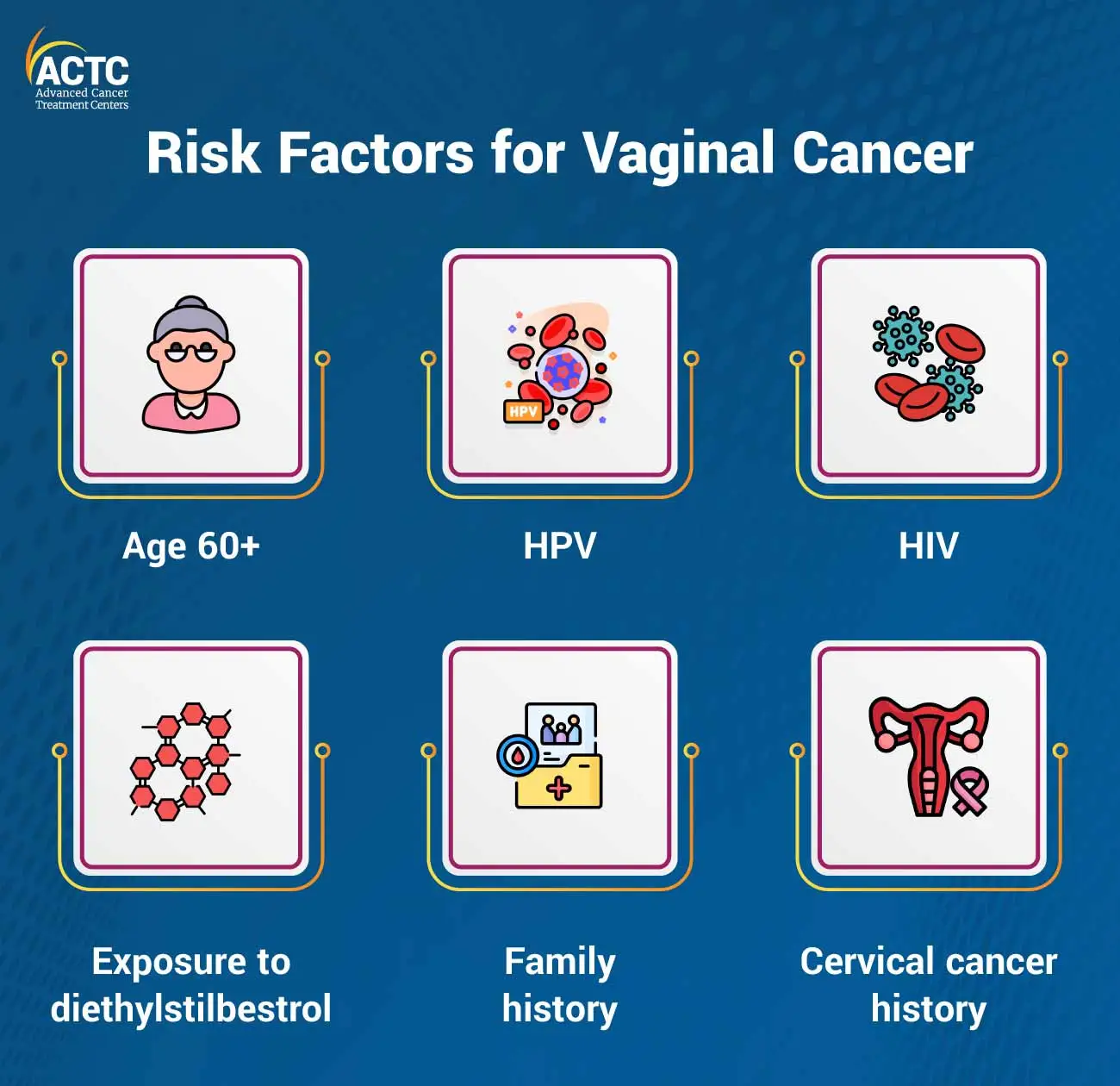
While most vaginal cancer cases are said to be caused by human papillomavirus or HPV infection, a few other factors can also increase the risk of this disease. The following are some common causes and risk factors for vaginal cancer:
Vaginal cancer symptoms are often not visible at the early stages of the disease. However, when cancer reaches a more advanced stage, the following symptoms can indicate the presence of cancerous cells in the vagina:
However, these symptoms are common for a few other conditions, and they do not necessarily indicate the presence of cancer. Individuals experiencing any of these symptoms should seek medical attention to get the right diagnosis and treatment in time.
During a routine pelvic exam or pap smear, if a primary care physician finds anything unusual, they may want to take a closer look by performing a colposcopy. To confirm the diagnosis, they may also recommend a biopsy test that involves taking out a tissue sample to detect the presence of cancerous cells.
Healthcare providers generally recommend imaging tests to find out the stage of cancer after a confirmed diagnosis. Imaging tests can help them determine whether the cancer is localized or is metastasized and has spread to other parts of the body. The following are the stages of vaginal cancer:
This is the most common treatment option for vaginal cancer where surgeons generally remove the affected tissue or abnormal growths in the vagina as much as they can. In more advanced cases, they may need to remove all or part of the vagina or perform a partial or complete hysterectomy to remove the cervix and uterus.
Oncologists generally recommend radiation therapy to effectively destroy affected tissues or cells that were impossible to remove through surgery. In external beam radiation therapy for cancer, a machine is used to send X-rays into the body to kill cancerous cells. In internal beam radiation therapy, a radiation therapist may insert a radioactive substance inside the body, on or near the cancer-affected cells.
However, radiation treatments can lead to severe side effects by damaging the ovaries and adjacent healthy cells and tissues. Therefore, it is crucial to discuss all possible treatment options in detail with an oncologist to consider the most suitable option.
It uses medication, either orally or through IV, to destroy or stop the growth of cancer-affected cells. Chemotherapy can also contribute to several side effects such as nausea, hair loss, changes in body weight, etc. These side effects usually improve or go away entirely over time once the treatment is completed.
The survival rate and prognosis depend on a number of factors, especially on the stage at which the cancer is detected.
The numbers show that at the early stages, vaginal cancer is highly curable and has a low recurrence rate. According to the American Cancer Society, the 5-year survival rate for localized (cancer that has not spread beyond the vagina) cancer stands at 87%.
However, for regional (cancer that has spread to nearby lymph nodes or tissues), and distant (cancer that has spread to distant organs or tissues) vaginal cancer cases, the number comes down to 47% and 9% respectively.
Although vaginal cancer is more prevalent in older women, it can affect women of all ages. Therefore, it is time to understand the importance of taking preventative measures, such as getting regular pap smears and HPV vaccinations. Additionally, staying aware of the symptoms of vaginal cancer and seeking medical attention promptly can improve the chances of a positive outcome from treatment. For any queries or concerns about vaginal cancer, contact ACTC, one of the best cancer treatment centers in Florida, providing personalized cancer care. To receive comprehensive cancer treatment, visit our website or call us at 352-345-4565 to schedule an appointment with our cancer care specialists.



January 07, 2026
A chemo port is a small device placed under your skin that makes recei...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
It's natural to wonder if testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is sa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A rash that will not calm down is scary, especially when it changes or...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Florida’s lung cancer burden remains significant and affects many fa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A partial hysterectomy, also called a supracervical hysterectomy, is s...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Finding a rash on your breast can be unsettling, but remember, many ra...
KNOW MORE
