
Book a Consultation
Thank you!
Your form has been sent successfully.



September 08, 2025
A brain tumor is a mass or growth of abnormal cells inside or near your brain. How a tumor affects you depends on its type, growth speed, and exact location.
Tumor symptoms differ widely based on these factors, and treatment is personalized to your situation. Doctors choose therapies considering the tumor’s size, location, biology (lab features), and your overall health.
Brain tumors are generally divided into two types depending on their origin.
Primary brain tumors start in the brain itself or in nearby tissues like the brain coverings (meninges), cranial nerves, or glands (such as the pituitary or pineal gland).
In adults, primary brain tumors occur less often than tumors that have spread from elsewhere. There are many types of primary tumors, usually named after the cell or tissue from which they arise.
Metastatic brain tumors start elsewhere in your body, then spread to the brain. They are more common than primary tumors among adults, especially those with a history of cancer.
Almost any type of cancer can spread to the brain. Common ones include:

Brain tumor symptoms depend heavily on the type, size, and location of the tumor. However, many of these symptoms may also have common non-tumor causes. That’s why it’s important to seek the care of a healthcare professional.
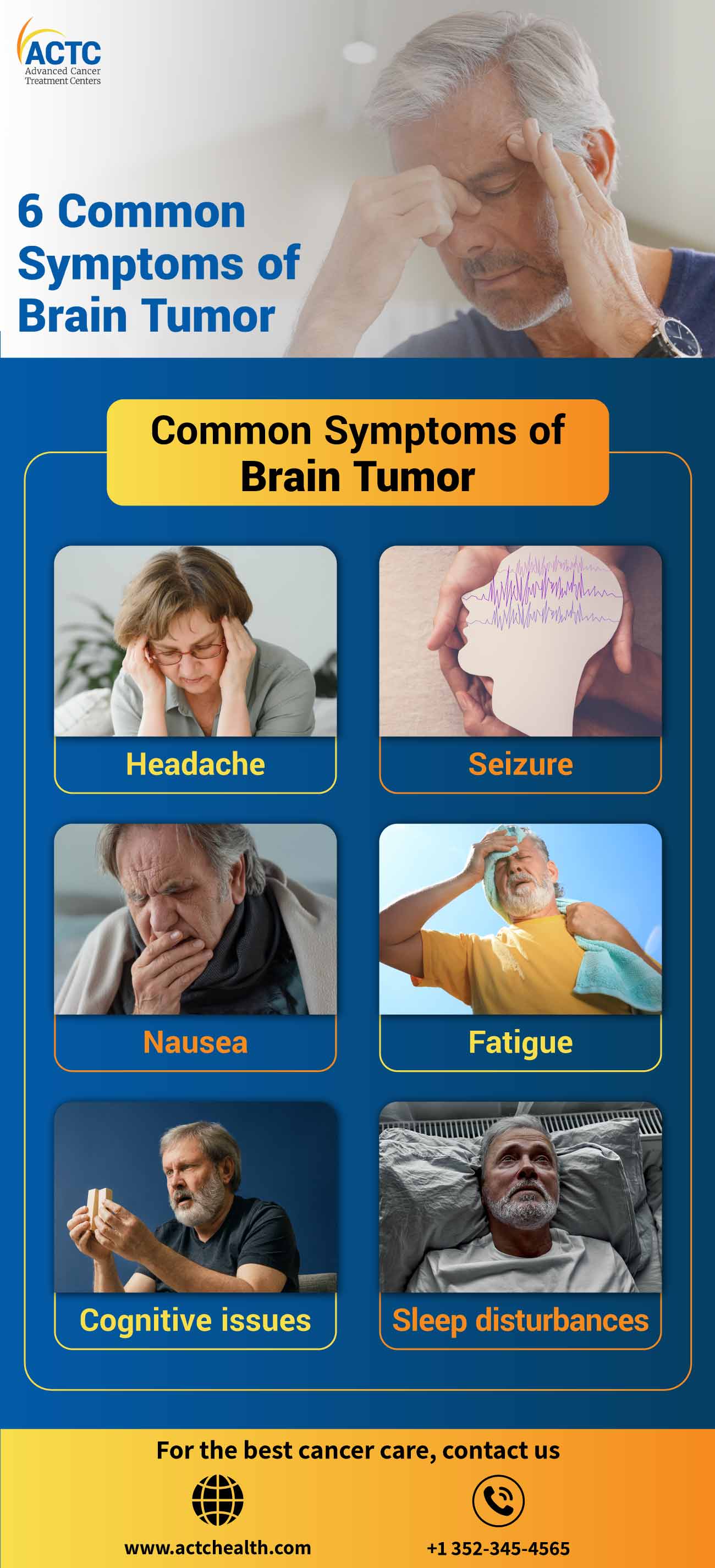
Here are common symptoms linked to brain tumors:
A brain tumor can lead to headaches by putting pressure on sensitive nerves and blood vessels or by blocking fluid flow, increasing pressure inside the head.
Tumor-related headaches often have unique patterns, such as:
Seizures happen due to sudden bursts of abnormal brain activity. They may be one of the first noticeable signs of a brain tumor.
Around half of people with brain tumors will experience seizures at some stage. Common seizure symptoms include:
Tumors can trigger nausea and vomiting due to increased pressure near your brain’s lower center (brainstem), which controls vomiting. Hormonal changes from tumors in areas like the pituitary gland can also cause nausea.
Severe vomiting, especially alongside other neurological symptoms like headaches or dizziness, needs prompt medical evaluation.
Brain tumors sometimes affect your thinking and memory, depending on where they form. Tumors in the frontal or parietal lobes can disrupt your ability to reason, plan, or make decisions.
Possible cognitive symptoms include:
These changes can result from many causes beyond tumors, including stress, medications, or vitamin deficiencies, so it’s important to talk to a doctor about persistent symptoms.
Changes in sleep habits are common for people with brain tumors. Difficulty sleeping often occurs along with fatigue or thinking problems. Experts continue to research the exact reasons for these sleep disturbances.
Common sleep issues include:
These issues may worsen other symptoms, such as fatigue or cognitive difficulties.
Fatigue from a brain tumor often feels deeper and more persistent than normal tiredness. You might feel constantly drained, heavy, or unable to recharge with rest.
Other signs of tumor-related fatigue include:
This kind of fatigue can seriously impact daily activities and quality of life.
The specific location of a brain tumor strongly influences the symptoms you experience. Certain parts of your brain control particular functions, and tumors in these areas may affect your ability to carry out everyday tasks.
| Tumor Location | Possible Symptoms or Changes |
| Pituitary gland, optic nerve, occipital lobe, temporal lobe | Vision problems (blurry vision, loss of sight, visual disturbances) |
| Temporal lobe, parietal lobe | Difficulties with speech, reading, or writing |
| Cranial nerves, temporal lobe | Hearing loss or auditory disturbances |
| Cerebellum, cranial nerves | Difficulty swallowing or speaking clearly |
| Cerebellum, frontal lobe, brainstem | Trouble with movement, coordination, or weakness in arms or legs |
| Cerebellum, brainstem, base of the brain | Issues with balance or coordination |
These location-specific symptoms help doctors pinpoint the area of concern, guiding diagnosis and treatment.
Brain tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Symptoms vary widely, but recognizing changes early and seeking prompt medical attention greatly improves treatment outcomes.
Your care team will develop a personalized plan based on your tumor’s specific features and your overall health.
Schedule an appointment or call Advanced Cancer Treatment Centers at 352-345-4565 to consult the best oncologists in Brooksville, Florida.


January 07, 2026
A chemo port is a small device placed under your skin that makes recei...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
It's natural to wonder if testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is sa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A rash that will not calm down is scary, especially when it changes or...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Florida’s lung cancer burden remains significant and affects many fa...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
A partial hysterectomy, also called a supracervical hysterectomy, is s...
KNOW MORE

December 24, 2025
Finding a rash on your breast can be unsettling, but remember, many ra...
KNOW MORE
